Anti-Bromodeoxyuridine mAb
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| MBL-MI-11-3 | 100 ug | £296.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Mouse
Antibody Isotype: IgG1
Antibody Clonality: Monoclonal
Antibody Clone: 2B1
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Human
Applications:
- Flow Cytometry
- Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Shipping:
4°C
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Applications:
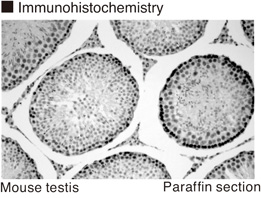
FCM - 10 ug/mL (final concentration) ICC - It is reported that this monoclonal antibody can be used in this application in the reference number 1). IHC - 10 ug/mL
Background:
BrdU (5-Bromo-2-Deoxyuridine) is a derivative of uridine that can substitute for thymidine during DNA synthesis. The detection of BrdU incorporation into DNA is a common method to quantify newly synthesized DNA and to identify cells in the S-phase of the cell cycle. BrdU incorporation is frequently used in proliferation assays to study DNA repair, sister chromatid exchange, and the cytokinetics of normal and neoplastic cells.
Concentration:
1 mg/mL
Formulation:
100 ug IgG in 100 ul volume of PBS containing 50% glycerol, pH 7.2. No preservative is contained.
Immunogen Translated:
5-Iodouridine-Ovalbumin
Reactivity:
This antibody reacts with bromodeoxyuridine incorporated in the nuclei in Raji cells on Flow cytometry and it reacts with iododeoxyuridine, iodouridine and bromouridine, but does not react with thymidine on Flow cytometry and Immunohistochemistry.
Shelf Life:
1 year
Source:
This antibody was purified from hybridoma (clone 2B1) supernatant using protein A agarose. This hybridoma was established by fusion of mouse myeloma cell P3U1 with Balb/c mouse splenocyte immunized with 5-iodouridine-Ovalbumin.
Target:
BrdU
References
1) Tani, H., et al., PLoS One 8, e55684 (2013) [RNA-IP]
2) Tani, H., et al., RNA Biol. 9, 1370-1379 (2012) [RNA-IP]
3) Yamazaki, S., et al.,EMBO J. 31, 3667-3677 (2012)[IC, DNA-IP]
4) Sugimura, K., et al., J. Cell Biol. 183, 1203-1212 (2008) [IC]
5) D?Ambrosio,C., et al., Genes Dev. 22, 2215-2227 (2008)[DNA-IP]
6) Bermejo, R., et al. Genes Dev. 21, 1921-1936 (2007) [DNA-IP]
7) Hirai, S., et al., J. Neurosci. 26, 11992-12002 (2006) [IHC]
8) Yamashita, N., et al., J. Neurosci. 26, 13357-13362 (2006) [IHC]
9) Yeom, S. Y., et al., Mol. Cell. Biol. 26, 4553-4563 (2006) [IHC]
10) Imai, F., et al., Development 133, 1735-1744 (2006) [IHC]
11) Itakura, E., et al., Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 5551-5562 (2005) [IF]
12) Katou, Y., et al., Nature 424, 1078-1083 (2003) [DNA-IP]
13) Ito, S., et al., J. Gen. Virol. 83, 2377-2383 (2002) [IC]
14) Liu, Q., et al., Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 6229-6239 (1999) [FCM]
15) Nakajima, T., et al., PNAS 95, 10590-10595 (1998) [FCM]
16) Gonchoroff, N. J., et al., J. Immunol. Meth. 93, 97-101 (1986)
17) Gonchoroff, N. J., et al., Cytometry 6, 506-512 (1985)
18) Gratzner, H. G., et al., Cytometry 1, 385-389 (1981)