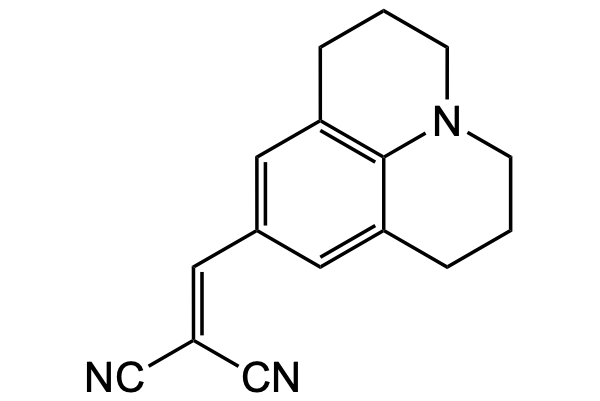
4-Dicyanovinyljulolidine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-D0113-M010 | 10 mg | £115.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C, Long term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
4-Dicyanovinyljulolidine; 9-Julolidinylmethylenmalononitril
Appearance:
Orange to very dark red powder.
CAS:
58293-56-4
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChi=1S/C16H15N3/c17-10-13(11-18)7-12-8-14-3-1-5-19-6-2-4-15(9-12)16(14)19/h7-9H,1-6H2
InChiKey:
LROAUBRDKLVBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 58293-56-4. Formula: C16H15N3. MW: 249.31. DCVJ is a fluorogenic dye that is considered a fluorescent molecular rotor because its properties depend on the rotational relaxation of the molecule, which can be influenced by the viscosity of the solvent used (quantum yield increases by decreasing free rotation). It has an excitation maximum at approximately 450 nm, and its emission is approximately 480 or 505 nm for low or high viscosity solvents, respectively. DCVJ has been used to study tubulin dynamics, it binds to tubulin and actin, and increases its fluorescence intensity drastically upon polymerization. DCVJ also binds to phospholipid bilayers, it integrates into the cell membrane and changes its quantum yield with the viscosity of the environment.
MDL:
MFCD01747392
Molecular Formula:
C16H15N3
Molecular Weight:
249.31
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
DCVJ is a fluorogenic dye that is considered a fluorescent molecular rotor because its properties depend on the rotational relaxation of the molecule, which can be influenced by the viscosity of the solvent used (quantum yield increases by decreasing free rotation). It has an excitation maximum at approximately 450 nm, and its emission is approximately 480 or 505 nm for low or high viscosity solvents, respectively. DCVJ has been used to study tubulin dynamics, it binds to tubulin and actin, and increases its fluorescence intensity drastically upon polymerization. DCVJ also binds to phospholipid bilayers, it integrates into the cell membrane and changes its quantum yield with the viscosity of the environment.
Purity:
>97% (HPLC)
SMILES:
N#C\C(=C/c1cc2CCCN3CCCc(c1)c23)C#N
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (20mg/ml) or chloroform.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Number:
41105331
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
(1) C.E. Kung & J.K. Reed; Biochem. 28, 6678 (1989) | (2) A. Bhattacharyya, et al.; Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 32, 442 (1995) | (3) M.A. Haidekker, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 278, H1401 (2000) | (4) J.A. Levitt, et al.; Chemphyschem 12, 662 (2011)