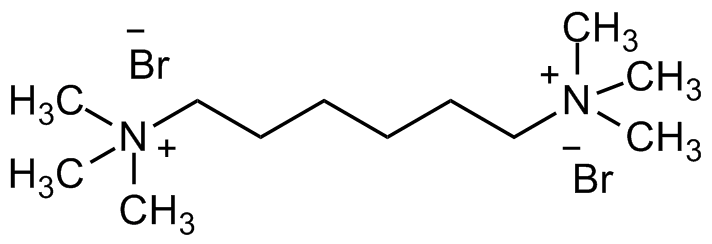
Hexamethonium bromide
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-H0455-G025 | 25 g | £68.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-H0455-G100 | 100 g | £184.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +20°C, Long term: +20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
N,N,N,N',N',N'-Hexamethylhexamethylenediammonium dibromide; Hexane-1,6-bis(trimethylammonium bromide)
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
55-97-0
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Keep under inert gas.Very hygroscopic.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C12H30N2.2BrH/c1-13(2,3)11-9-7-8-10-12-14(4,5)6;;/h7-12H2,1-6H3;2*1H/q+2;;/p-2
InChiKey:
FAPSXSAPXXJTOU-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 55-97-0. Formula: C12H30Br2N2. MW: BD9837. Hexamethonium bromide is a peripherally-acting nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent that acts as a non-competitive antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). Formulations containing hexamethonium were previously used in the treatment of hypertension. Induces apoptosis and inhibits the stimulatory effect of nicotine on endothelial cell DNA synthesis and proliferation.
MDL:
MFCD00011787
Molecular Formula:
C12H30Br2N2
Molecular Weight:
362.19
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Hexamethonium bromide is a peripherally-acting nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent that acts as a non-competitive antagonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). Formulations containing hexamethonium were previously used in the treatment of hypertension. Induces apoptosis and inhibits the stimulatory effect of nicotine on endothelial cell DNA synthesis and proliferation.
Purity:
>98% (TLC)
SMILES:
C[N+](C)(C)CCCCCC[N+](C)(C)C.[Br-].[Br-]
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (30mg/ml) or DMSO (10mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
References
(1) A.R. Hunter; Lancet 1, 251 (1950) | (2) J.A. Gosling & T.C. Lu; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 167, 56 (1969) | (3) A.C. Villablanca; J. Appl. Physiol. 84, 2089 (1998) | (4) P. Dasgupta, et al.; PNAS 103, 6332 (2010) | (5) Y. Nishida, et al.; J. Physiol. Sci. 62, 147 (2012)