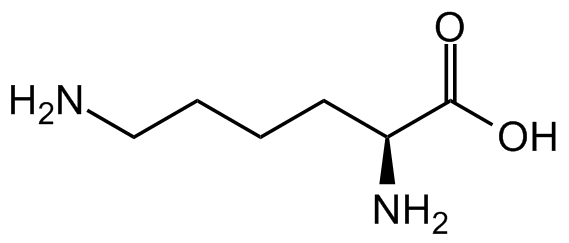
L-Lysine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-L0110-G001 | 1 g | £68.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Plant
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +20°C, Long term: +20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
H-Lys-OH; (S)-Lysine; (S)-2,6-Diaminocaproic acid
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
56-87-1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Keep under inert gas.Very hygroscopic.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C6H14N2O2/c7-4-2-1-3-5(8)6(9)10/h5H,1-4,7-8H2,(H,9,10)/t5-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 56-87-1. Formula: C6H14N2O2. MW: BD9837. L-Lysine is an essential alpha-amino acid, which is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. It is a key building block in protein synthesis in which it acts as a base. Lysine residues are useful in many cellular processes, due to their ability to accept a wide variety of post-translational modifications. These modifications include acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, neddylation, biotinylation, pupylation and carboxylation. L-lysine is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by humans and mammals through transamination. Lysine plays a pivotal role in different processes inside the human body, such as proteinogenesis, catalysis, fatty acid metabolism, histone modification, polypeptide crosslinking, calcium homeostasis, and acts as a nucleophile in enzymatic reactions. Because of its pivotal role in promoting growth and development, enhancing immunity, and preventing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, L-lysine is used in food health care, feed additives and pharmaceutical preparations.
MDL:
MFCD00064433
Molecular Formula:
C6H14N2O2
Molecular Weight:
146.19
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
L-Lysine is an essential alpha-amino acid, which is encoded by the codons AAA and AAG. It is a key building block in protein synthesis in which it acts as a base. Lysine residues are useful in many cellular processes, due to their ability to accept a wide variety of post-translational modifications. These modifications include acetylation, methylation, ubiquitination, sumoylation, neddylation, biotinylation, pupylation and carboxylation. L-lysine is an essential amino acid that cannot be synthesized by humans and mammals through transamination. Lysine plays a pivotal role in different processes inside the human body, such as proteinogenesis, catalysis, fatty acid metabolism, histone modification, polypeptide crosslinking, calcium homeostasis, and acts as a nucleophile in enzymatic reactions. Because of its pivotal role in promoting growth and development, enhancing immunity, and preventing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, L-lysine is used in food health care, feed additives and pharmaceutical preparations.
Purity:
>98% (TLC)
SMILES:
NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Fermented from plant source.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at RT.
References
(1) M. Smriga & K. Torii; PNAS 100, 15370 (2003) | (2) L. Tosha, al.: Biochem. J. 435, 509 (2011) | (3) F.-M. Boisvert, et al.; Mol. Cell Proteomics 11, M111.011429 (2012) | (4) F.K.D.C Felix, et al.; Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 39, 1031 (2019) | (5) K. Hayamizu, et al.; J. Nutr. 150, 2561S (2020) | (6) D. Zhang, et al.; J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 3189 (2021) | (7) Q. Li, et al.; Molecules 27, 35209157 (2022) | (8) S. Muduli, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. acta 1867, 130320 (2023)