AOH1996
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3553-M005 | 5 mg | £120.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3553-M025 | 25 mg | £350.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C, Long term: -20°C.
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
NSC789796; N-(2-((2-(3-Methoxyphenoxy)phenyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)-1-naphthamide
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
2089314-64-5
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C26H22N2O4/c1-31-19-10-7-11-20(16-19)32-24-15-5-4-14-23(24)28-25(29)17-27-26(30)22-13-6-9-18-8-2-3-12-21(18)22/h2-16H,17H2,1H3,(H,27,30)(H,28,29)
InChiKey:
HDMONPHKMIZXDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 2089314-64-5. Formula: C26H22N2O4. MW: BD9837. AOH1996 is an orally available and metabolically stable small molecule PCNA inhibitor, which selectively kills cancer cells, with a median concentration of about 300 nM for 50% growth inhibition. AOH1996 was not significantly toxic to non-malignant cells, even up to 10 uM. AOH1996 enhances the interaction between PCNA and the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII), RPB1, and dissociates PCNA from actively transcribed chromatin regions, while inducing DNA double-stranded breaks in a transcription-dependent manner, leading to the overall degradation of RPB1 and the collapse of replication forks in actively transcribed regions. AOH1996 was created to target a post-translationally modified isoform of PCNA, termed caPCNA, which is preferentially found in cancer cells. PCNA is crucial in the body for DNA repair, but targeting it is difficult because of its role in healthy cells. By selectively targeting caPCNA, it may be possible to kill cancer cells without affecting healthy tissues. In vitro testing demonstrated that AOH1996 inhibited the growth and induced cell cycle arrest (G2/M or S phase arrest) and apoptotic cell death in a wide variety of cancer cell lines, but had no effect on several normal, nonmalignant cell types.
Molecular Formula:
C26H22N2O4
Molecular Weight:
426.5
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
AOH1996 is an orally available and metabolically stable small molecule PCNA inhibitor, which selectively kills cancer cells, with a median concentration of about 300 nM for 50% growth inhibition. AOH1996 was not significantly toxic to non-malignant cells, even up to 10 uM. AOH1996 enhances the interaction between PCNA and the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII), RPB1, and dissociates PCNA from actively transcribed chromatin regions, while inducing DNA double-stranded breaks in a transcription-dependent manner, leading to the overall degradation of RPB1 and the collapse of replication forks in actively transcribed regions. AOH1996 was created to target a post-translationally modified isoform of PCNA, termed caPCNA, which is preferentially found in cancer cells. PCNA is crucial in the body for DNA repair, but targeting it is difficult because of its role in healthy cells. By selectively targeting caPCNA, it may be possible to kill cancer cells without affecting healthy tissues. In vitro testing demonstrated that AOH1996 inhibited the growth and induced cell cycle arrest (G2/M or S phase arrest) and apoptotic cell death in a wide variety of cancer cell lines, but had no effect on several normal, nonmalignant cell types.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
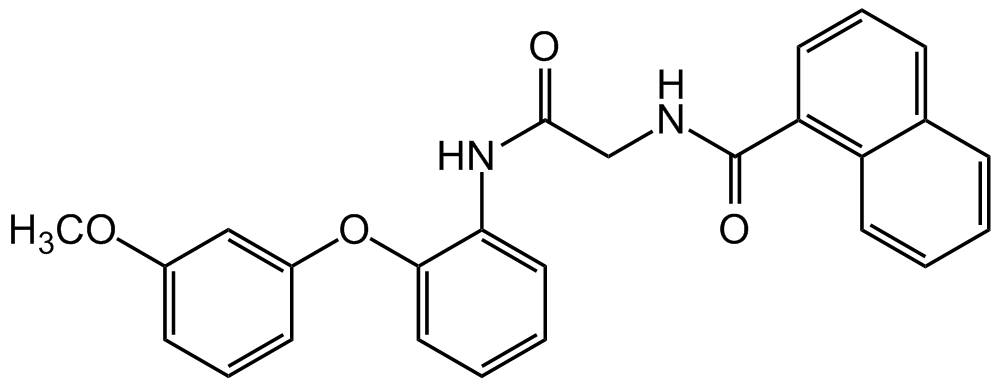
O=C(CNC(C1=C(C=CC=C2)C2=CC=C1)=O)NC3=CC=CC=C3OC4=CC(OC)=CC=C4
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
The Anticancer Activity of a First-in-class Small-molecule Targeting PCNA: L. Gu, et al.; Clin. Cancer Res. 24, 6053 (2018) | Small molecule targeting of transcription-replication conflict for selective chemotherapy: L. Gu, et al.; Cell Chem. Biol. (Epub ahead of print) (2023) | Arginine shortage induces replication stress and confers genotoxic resistance by inhibiting histone H4 translation and promoting PCNA ubiquitination: Y.-C. Wang, et al.; Cell Rep. 42, 112296 (2023) | Therapeutic Targeting of DNA Replication Stress in Cancer: L. Gu, et al.; Genes 14, 1346 (2023) (Review)