Nocodazole
Product Code:
AG-CR1-0019
AG-CR1-0019
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
4°C
4°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-0019-M005 | 5 mg | £40.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-0019-M010 | 10 mg | £60.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-0019-M025 | 25 mg | £95.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-0019-M050 | 50 mg | £160.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
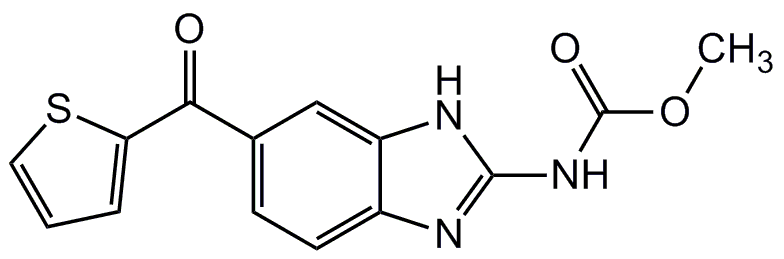
Methyl[5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
31430-18-9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS08
Hazards:
H341, H351
InChi:
InChI=1S/C14H11N3O3S/c1-20-14(19)17-13-15-9-5-4-8(7-10(9)16-13)12(18)11-3-2-6-21-11/h2-7H,1H3,(H2,15,16,17,19)
InChiKey:
KYRVNWMVYQXFEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 31430-18-9. Formula: C14H11N3O3S. MW: 301.3. Microtubule inhibitor. Antitumor compound. Mitosis inhibitor. Arrests the cell cycle at G2/M phase. Promotes tubulin depolymerization. Induces fragmentation of the Golgi complex. Inhibits the T cell antigen receptor. Stimulates the intrinsic GTPase activity of tubulin. Activates the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Apoptosis inducer. Autophagy inhibition through prevention of autophagosome-lysosome fusion.
MDL:
MFCD00005588
Molecular Formula:
C14H11N3O3S
Molecular Weight:
301.3
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P201, P202, P281, P308, P313, P405
Product Description:
Microtubule inhibitor [1, 2, 4]. Antitumor compound [1, 2]. Mitosis inhibitor [3]. Arrests the cell cycle at G2/M phase [9]. Promotes tubulin depolymerization [4]. Induces fragmentation of the Golgi complex [5]. Inhibits the T cell antigen receptor [6]. Stimulates the intrinsic GTPase activity of tubulin [7]. Activates the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway [8]. Apoptosis inducer [10, 11]. Autophagy inhibition through prevention of autophagosome-lysosome fusion.
Purity:
>98% (NMR)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
COC(=O)NC1=NC2=CC=C(C=C2N1)C(=O)C1=CC=CS1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or dimethylformamide; almost insoluble in water.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
Documents
References
R17934-NSC 238159: a new antitumor drug--I. Effect on experimental tumors and factors influencing effectiveness: G. Atassi and H.J. Tagnon; Eur. J. Cancer 11, 599 (1975) | R17934-NSC238159: a new antitumor drug--II. Effect on mitotic cycle of L1210 leukemia cells in vivo and synergism with cytosine arabinoside (NSC63878): G. Atassi, et al.; Eur. J. Cancer 11, 609 (1975) | Effects of vinblastine, podophyllotoxin and nocodazole on mitotic spindles. Implications for the role of microtubule dynamics in mitosis; M.A. Jordan, et al.; J. Cell Sci. 102, 401 (1992) | Nanomolar concentrations of nocodazole alter microtubule dynamic instability in vivo and in vitro: R.J. Vasquez, et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell 8, 973 (1997) | Recycling of golgi-resident glycosyltransferases through the ER reveals a novel pathway and provides an explanation for nocodazole-induced Golgi scattering: B. Storrie, et al.; J. Cell Biol. 143, 1505 (1998) | Nocodazole inhibits signal transduction by the T cell antigen receptor: R.D. Huby, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 273, 12024 (1998) | Studies on the nocodazole-induced GTPase activity of tubulin: M.R. Mejillano, et al.; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 336, 130 (1996) | Microtubule-interfering agents activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase through both Ras and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase pathways: T.H. Wang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 273, 4928 (1998) | Raf-1/MEK/MAPK pathway is necessary for the G2/M transition induced by nocodazole: C. Hayne, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 275, 31876 (2000) | Apoptosis induced by microtubule disrupting drugs in normal murine thymocytes in vitro: V. Bumbasirevic, et al.; Scanning Microsc. 9, 509 (1995) | Nocodazole induces mitotic cell death with apoptotic-like features in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: K. Endo, et al.; FEBS Lett. 584, 2387 (2010)