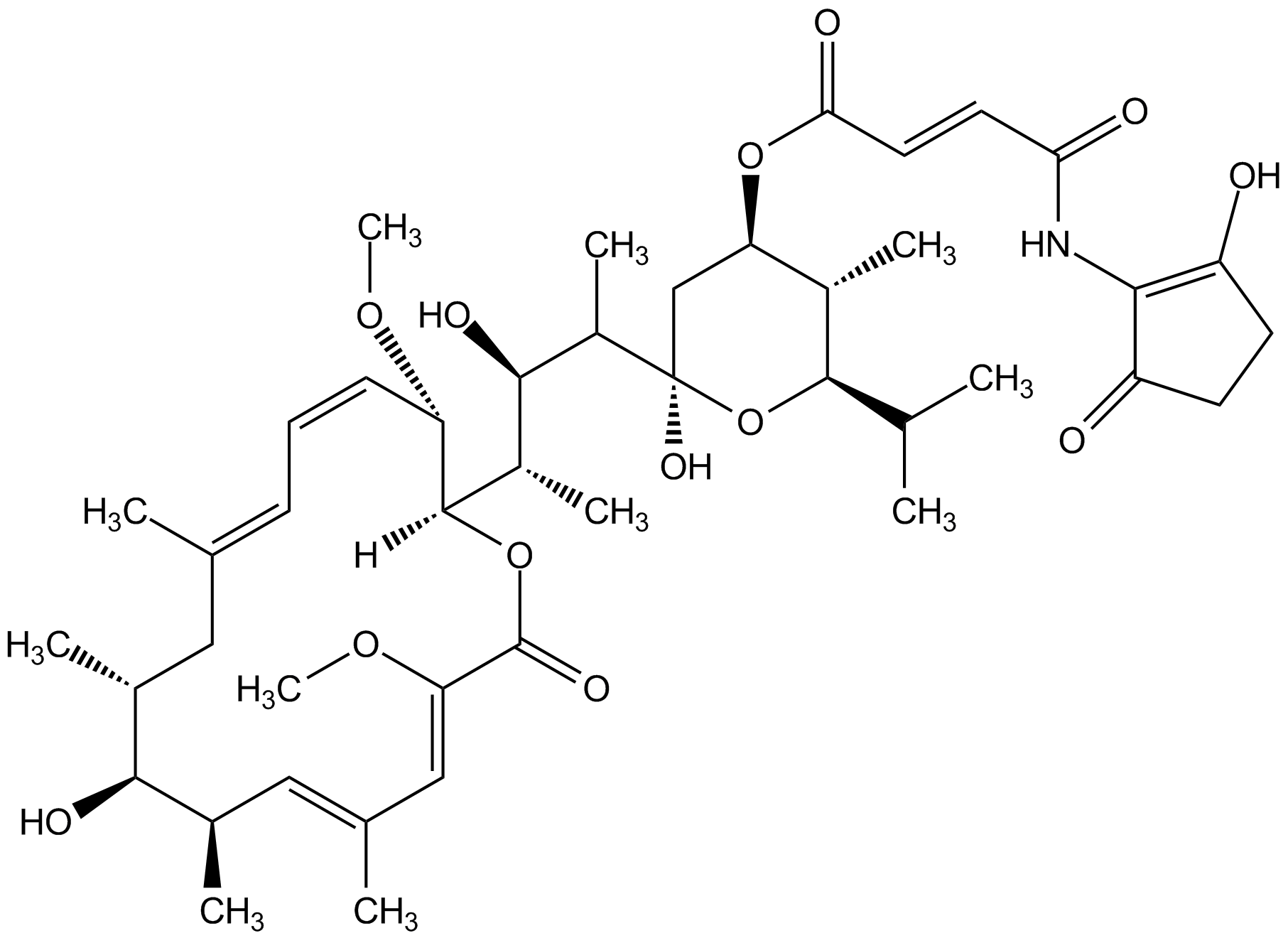
Bafilomycin B1
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| BVT-0004-C100 | 100 ug | £65.00 |
Quantity:
| BVT-0004-M001 | 1 mg | £105.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
20°C
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Setamycin; BRN4640118
Appearance:
Yellow solid.
CAS:
88899-56-3
Class:
6.1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS06
Handling Advice:
Protect from light when in solution.
Hazards:
H300, H310, H319, H332
InChi:
InChI=1S/C44H65NO13/c1-23(2)41-28(7)35(56-37(49)18-17-36(48)45-38-31(46)15-16-32(38)47)22-44(53,58-41)30(9)40(51)29(8)42-33(54-10)14-12-13-24(3)19-26(5)39(50)27(6)20-25(4)21-34(55-11)43(52)57-42/h12-14,17-18,20-21,23,26-30,33,35,39-42,46,50-51,53H,15-16,19,22H2,1-11H3,(H,45,48)/b14-12-,18-17+,24-13+,25-20+,34-21-/t26-,27-,28+,29+,30?,33+,35-,39+,40-,41-,42-,44-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
KFUFLYSBMNNJTF-APLCIVFZSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 88899-56-3. Formula: C44H65NO13. MW: 815.9. Isolated from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Macrolide antibiotic. Specific vacuolar-type H+-ATPase inhibitor. Inhibitor of autophagic degradation by rising lysosomal pH and thus inactivating the lysosomal acid hydrolases. Antitrypanosomal and antileishmanial compound. Phytotoxic. Influences the cell wall biosynthesis of Asp. niger.
MDL:
MFCD32197371
Molecular Formula:
C44H65NO13
Molecular Weight:
815.9
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
PG:
III
Precautions:
P261, P262, P280, P301, P310, P302, P350, P312
Product Description:
Macrolide antibiotic. Specific vacuolar-type H+-ATPase inhibitor. Inhibitor of autophagic degradation by rising lysosomal pH and thus inactivating the lysosomal acid hydrolases. Antitrypanosomal and antileishmanial compound. Phytotoxic. Influences the cell wall biosynthesis of Asp. niger.
Purity:
>97% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Danger
SMILES:
[H][C@@]1(OC(=O)C(OC)=CC(C)=C[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](C)CC(C)=CC=C/[C@@H]1OC)[C@@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@H](C)[C@@]1(O)C[C@@H](OC(=O)C=CC(=O)NC2=C(O)CCC2=O)[C@H](C)C(O1)C(C)C
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or acetone. Insoluble in water. Unstable in methanol.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Streptomyces hygroscopicus.
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
UN 3462
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C.
References
Metabolic products of microorganisms. 224. Bafilomycins, a new group of macrolide antibiotics. Production, isolation, chemical structure and biological activity: G. Werner, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 37, 110 (1984) | Inhibitory effect of modified bafilomycins and concanamycins on P- and V-type adenosinetriphosphatases: S. Drose, et al.; Biochemistry 32, 3902 (1993) | Bafilomycins and concanamycins as inhibitors of V-ATPases and P-ATPases: S. Drose and K. Altendorf; J. Exp. Biol. 200, 1 (1997) | Biosynthetic investigations of the V-type ATPase inhibitors bafilomycin A1, B1 and concanamycin A: T. Schuhmann and S. Grond; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 57, 655 (2004) | Autophagy, bafilomycin and cell death: the "a-B-cs" of plecomacrolide-induced neuroprotection: J.J. Shacka, et al.; Autophagy 2, 228 (2006) | Bafilomycins produced in culture by Streptomyces spp. isolated from marine habitats are potent inhibitors of autophagy: G. Carr, et al.; Journal of Nat. Prod. 73, 422 (2010) | Low-dose bafilomycin attenuates neuronal cell death associated with autophagy-lysosome pathway dysfunction: V. N. Pivtoraiko; J. Neurochem. 114, 1193 (2010) | Vacuolar H(+)-ATPase plays a keyrole in cell wall biosynthesis of Aspergillus niger: D. Schachtschabel, et al.; Fungalgenet. Biol. 49, 284 (2012) | Characterization of the bafilomycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces lohii: W. Zhang, et al.; ChemBioChem 14, 301 (2013) | Isolation and characterization of phytotoxic compounds produced by Streptomyces sp. AMC 23 from red mangrove(rhizophora mangle): E. Crevelin, et al.; Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 171, 1602 (2013) | High-throughput screening platform for natural product-based drug discovery against 3 neglected tropical diseases: human African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, and chagas disease: F. Annang, et al.; J. Biomol. Screen. 20, 82 (2015)