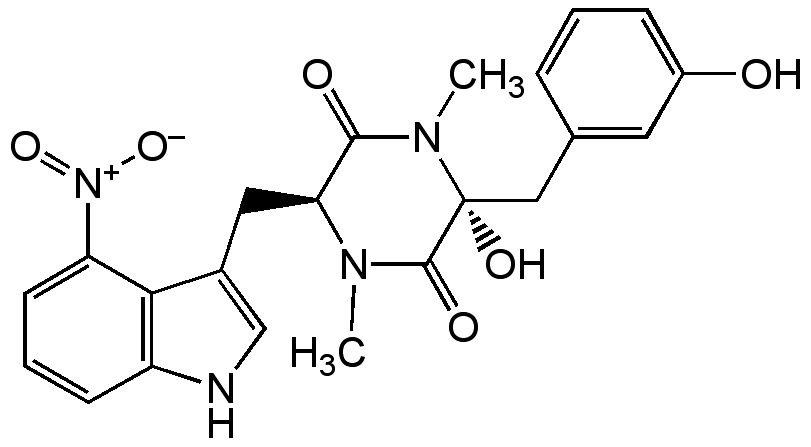
Thaxtomin A
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| BVT-0206-M001 | 1 mg | £205.00 |
Quantity:
| BVT-0206-M005 | 5 mg | £685.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
20°C
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Thaztomin A
Appearance:
Yellow powder.
CAS:
122380-18-1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Hazards:
H302, H312, H319, H332
InChi:
InChI=1S/C22H22N4O6/c1-24-18(10-14-12-23-16-7-4-8-17(19(14)16)26(31)32)20(28)25(2)22(30,21(24)29)11-13-5-3-6-15(27)9-13/h3-9,12,18,23,27,30H,10-11H2,1-2H3/t18-,22+/m0/s1
InChiKey:
QRDNJYNIEGRRKV-PGRDOPGGSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 122380-18-1. Formula: C22H22N4O6. MW: 438.4. Isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis G?-Dra 17. Diketopiperazine antibiotic. Phytotoxin. Herbicide. Natural cellulose synthesis inhibitor. Plant cell necrosis inducer. Induces common scab disease of potato.
MDL:
MFCD08457945
Molecular Formula:
C22H22N4O6
Molecular Weight:
438.4
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Precautions:
P261, P270, P280, P301, P312, P302, P352, P312
Product Description:
Diketopiperazine antibiotic. Phytotoxin. Herbicide. Natural cellulose synthesis inhibitor. Plant cell necrosis inducer. Induces common scab disease of potato.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
CN1[C@@H](CC2=CNC3=C2C(=CC=C3)[N+]([O-])=O)C(=O)N(C)[C@@](O)(CC2=CC(O)=CC=C2)C1=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or dimethyl formamide; partially soluble in methanol or 100% ethanol; poorly soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis G?-Dra 17.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C.
References
Isolation and characterization of phytotoxins associated with Streptomyces scabies: R. R. King, et al.; J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 13, 849 (1989) | An Arabidopsis mutant resistant to thaxtomin A, a cellulose synthesis inhibitor from Streptomyces species: W.R. Scheible, et al.; Plant Cell 15, 1781 (2003) | Thaxtomin A induces programmed cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana suspension-cultured cells: I. Duval, et al.; Planta 222, 820 (2005) | The Thaxtomin phytotoxins: Sources, synthesis, biosynthesis, biotransformation and biological activity: R. R. King & L. A. Calhoun; Phytochemistry 70, 833 (2009) (Review) | Streptomyces scabiei and its toxin thaxtomin A induce scopoletin biosynthesis in tobacco and Arabidopsis thaliana: S. Lerat, et. al.; Plant Cell Rep. 28, 1895 (2009) | Two different signaling pathways for Thaxtomin A-induced cell death in Arabidopsis and tobacco BY2: P. Meimoun, et al.; Plant Sign. Behav. 4, 142 (2009) | Relationship of resistance to common scab disease and tolerance to thaxtomin A toxicity within potato cultivars: R. S. Tegg, et al.; Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 128, 143 (2010) | Total synthesis of thaxtomin A and its stereoisomers and findings of their biological activities: H. Zhang, et al.; Org. Lett. 15, 5670 (2013) | Thaxtomin A production and virulence are controlled by several bld gene global regulators in Streptomyces scabies: D. Bignell, et al.; Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 27, 875 (2014) | Mechanisms of thaxtomin A-induced root toxicity revealed by a thaxtomin A sensitive Arabidopsis mutant (ucu2-2/gi-2): R.S. Tegg, et al.; Plant Cell Rep. 35, 347 (2016) | De novo biosynthesis of "non-natural" thaxtomin phytotoxins: M. Winn, et al.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 6830 (2018) | Evaluation of Streptomyces common scab toxins diffusion in potato tubers and through the intestinal barrier: C. Leclerc, et al.; Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 6, 1662 (2017) | The emergence of nitric oxide in the biosynthesis of bacterial natural products: J D. Caranto; Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 49, 130 (2019) | Chemical activation of EDS1/PAD4 signaling leading to pathogen resistance in Arabidopsis: S. Joglekar, et al.; Plant Cell Physiol. 59, 1592 (2018) | Reactive oxygen species alleviate cell death induced by thaxtomin A in Arabidopsis thaliana cell cultures: F. Awwad, et al.; Plants 8, 332 (2019)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Elmycin B | BVT-0198 | Bioviotica | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nargenicin A1 | BVT-0204 | Bioviotica | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||