G418 . sulfate
Product Code:
AG-CN2-0030
AG-CN2-0030
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
-20°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0030-M250 | 250 mg | £35.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0030-M500 | 500 mg | £45.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0030-G001 | 1 g | £55.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0030-G005 | 5 g | £160.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 7-10 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Geneticin; Antibiotic G418; BRN 1669188
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
Biological Activity:
Assay: >700 µg/mgBiological Assay: ED50 Resistant: >2500 µg/mlBiological Assay: ED50 Sensitivity: <400 µg/ml
CAS:
108321-42-2
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Hazards:
H302, H312, H332
InChi:
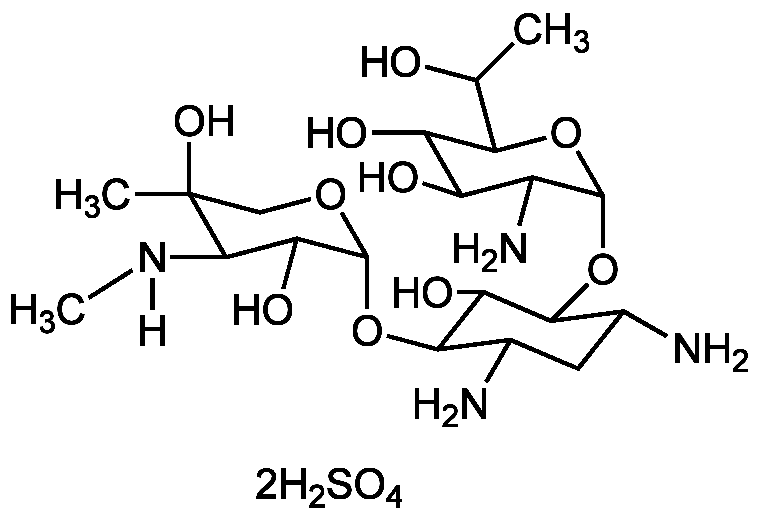
InChI=1S/C20H40N4O10/c1-6(25)14-11(27)10(26)9(23)18(32-14)33-15-7(21)4-8(22)16(12(15)28)34-19-13(29)17(24-3)20(2,30)5-31-19/h6-19,24-30H,4-5,21-23H2,1-3H3
InChiKey:
BRZYSWJRSDMWLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 108321-42-2. Formula: C20H40N4O10 . 2H2SO4. MW: 496.6 . 196.1. Isolated from Micromonospora rhodorangea. Antibiotic. Cytotoxic to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by inhibiting the protein synthesis. Apoptosis inducer. Widely employed in the selection of eukaryotic expression vectors, in combination with either aminoglycoside phosphotransferase 3' or APH II. Antiviral.
MDL:
MFCD05664725
Molecular Formula:
C20H40N4O10 . 2H2SO4
Molecular Weight:
496.6 . 196.1
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P280, P301, P312, P302, P352, P304, P340
Product Description:
Antibiotic [1]. Cytotoxic to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells by inhibiting the protein synthesis [1, 3, 4, 6]. Apoptosis inducer [5]. Widely employed in the selection of eukaryotic expression vectors, in combination with either aminoglycoside phosphotransferase 3' or APH II [2]. Antiviral [7, 8].
Purity:
>98% (TLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H]N(C)C1C(O)C(OC2C(N)CC(N)C(OC3OC(C(C)O)C(O)C(O)C3N)C2O)OCC1(C)O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (up to 50 mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Isolated from Micromonospora rhodorangea.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
Documents
References
Antibiotic G-418, a new Micromonospora-produced aminoglycoside with activity against protozoa and helminths: fermentation, isolation, and preliminary characterization: G.H. Wagman, et al.; Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 6, 144 (1974) | Phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C is activated allosterically by the aminoglycoside G418. 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-scyllo-inositol-1-O-dodecylphosphonate and its analogs inhibit glycosylphosphatidylinositol phospholipase C: J.C. Morris, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 271, 15468 (1996) | Addition of G418 and other aminoglycoside antibiotics to mammalian cells results in the release of GPI-anchored proteins: M. Kung, et al.; FEBS Lett. 409, 333 (1997) | The effects of G418 on the growth and metabolism of recombinant mammalian cell lines: C.A. Yallop & I. Svendsen; Cytotechnology 35, 101 (2001) | Cytochrome c release and endoplasmic reticulum stress are involved in caspase-dependent apoptosis induced by G418: Q.H. Jin, et al.; Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61, 1816 (2004) | Expression and distribution of HSP27 in response to G418 in different human breast cancer cell lines: L. Qian, et al.; Histochem. Cell Biol. 126, 593 (2006) | Antiviral activity of geneticin against bovine viral diarrhoea virus: A.V. Birk, et al.; Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 19, 33 (2008) | Antiviral activity of geneticin against dengue virus: X.G. Zhang, et al.; Antiviral Res. 83, 21 (2009)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Puromycin . 2HCl | AG-CN2-0078 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|