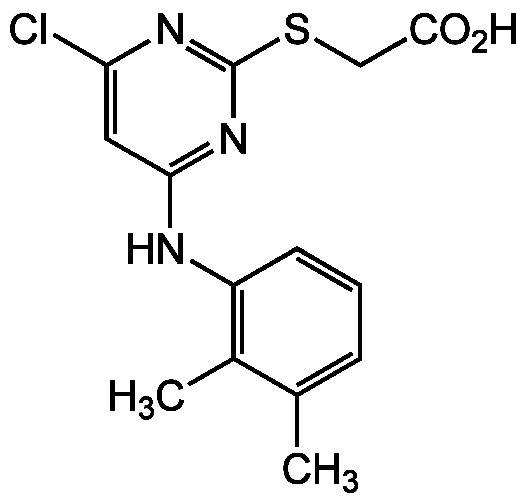
WY-14643
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3566-M010 | 10 mg | £30.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3566-M050 | 50 mg | £60.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3566-M250 | 250 mg | £170.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
-20°C
Storage:
+4deg;C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Pirinixic acid; NSC 310038; BRN 0759945; ((4-Chloro-6-((2,3-dimethylphenyl)amino)-2-pyrimidinyl)thio) acetic acid
Appearance:
Off-white solid.
CAS:
50892-23-4
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07,GHS08
Hazards:
H302, H315, H319, H335, H350
InChi:
InChI=1S/C20H29NO5S/c1-13-5-3-4-6-14(2)9-18(22)25-16-10-15(8-7-13)26-20(24,11-16)17-12-27-19(23)21-17/h3,5,9,13,15-17,24H,4,6-8,10-12H2,1-2H3,(H,21,23)/b5-3-,14-9-/t13-,15-,16-,17-,20-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
NSHPHXHGRHSMIK-WAXGXQFOSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 50892-23-4. Formula: C14H14ClN3O2S. MW: 323.8. Potent peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARalpha) activator. Activates also PPARgamma but not PPARdelta. Potent anti-hypercholesterolemic agent. Hypolipidemic compound. Lipogenesis inducer. Tumor promoter. Causes increased cell proliferation and decreased apoptosis. Anti-inflammatory. Inhibits NF-kappaB transcriptional activity and decreases the inflammatory response by reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL1beta). Reduces oxidative stress. Increases fatty acid oxidation. Directly affects insulin signaling. Increases glucose uptake. Reviews.
MDL:
MFCD00191335
Molecular Formula:
C14H14ClN3O2S
Molecular Weight:
323.8
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P280, P301, P312, P302, P352, P304, P340
Product Description:
Potent peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARalpha) activator [1, 2, 7, 9]. Activates also PPARgamma [4, 7] but not PPARdelta [8]. Potent anti-hypercholesterolemic agent [1]. Hypolipidemic compound. Lipogenesis inducer [2, 10]. Tumor promoter [2, 3, 5, 15]. Causes increased cell proliferation and decreased apoptosis [5]. Anti-inflammatory. Inhibits NF-kappaB transcriptional activity and decreases the inflammatory response by reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL1beta). Reduces oxidative stress [6, 7, 12, 13]. Increases fatty acid oxidation [11]. Directly affects insulin signaling. Increases glucose uptake [12]. Enhancer of ethanol metabolism. Reviews [5, 11, 14].
Purity:
>98%
Signal word:
Danger
SMILES:
CC1=CC=CC(NC2=NC(SCC(O)=O)=NC(Cl)=C2)=C1C
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in ethanol, DMSO, dimethyl formamide or PBS (pH 7.2).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
A potent antihypercholesterolemic agent: (4-chloro-6-(2,3-xylidino)-2-pyrimidinylthio) acetic acid (Wy-14643): A.A. Santilli, et al.; Experientia 30, 1110 (1974) | The hepatic effects of hypolipidemic drugs (clofibrate, nafenopin, tibric acid, and Wy-14,643) on hepatic peroxisomes and peroxisome-associated enzymes: D.E. Moody & J.K. Reddy; Am. J. Pathol. 90, 435 (1978) | Peroxisome proliferation and hepatocarcinogenesis: M.S. Rao & J.K. Reddy; Carcinogenesis 8, 631 (1987) | Identification of a new member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily that is activated by a peroxisome proliferator and fatty acids: A. Schmidt, et al.; Mol. Endocrinol. 6, 1634 (1992) | Non-genotoxic hepatocarcinogenesis: suppression of apoptosis by peroxisome proliferators: R.A. Roberts; Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 804, 588 (1996) (Review) | The PPARalpha-leukotriene B4 pathway to inflammation control: P.R. Devchand, et al.; Nature 384, 39 (1996) | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors a and g are activated by indomethacin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: J.M. Lehmann, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 272, 3406 (1997) | Hypolipidemic drugs, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and eicosanoids are ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and delta: B.M. Forman, et al.; PNAS 94, 4312 (1997) | Activation of human aortic smooth-muscle cells is inhibited by PPARalpha but not by PPARgamma activators: B. Staels, et al.; Nature 393, 790 (1998) | Influence of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonists on the intracellular turnover and secretion of apolipoprotein (Apo) B-100 and ApoB-48: D. Lind?n, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23044 (2002) | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) signaling in the gene regulatory control of energy metabolism in the normal and diseased heart: B.N. Finck & D.P. Kelly; J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 34, 1249 (2002) (Review) | WY-14643 and 9- cis-retinoic acid induce IRS-2/PI 3-kinase signalling pathway and increase glucose transport in human skeletal muscle cells: differential effect in myotubes from healthy subjects and Type 2 diabetic patients: K. Bouzakri, et al.; Diabetologia 47, 1314 (2004) | Oxidative stress and inflammatory response evoked by transient cerebral ischemia/reperfusion: effects of the PPAR-alpha agonist WY14643: M. Collino, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 41, 579 (2006) | Cardiovascular actions of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha) agonist Wy14,643: P. Zahradka; Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 25, 99 (2007) (Review) | PPARalpha: mechanism of species differences and hepatocarcinogenesis of peroxisome proliferators; F.J. Gonzalez & Y.M. Shah; Toxicology 246, 2 (2008) | PPARalpha agonist WY-14,643 enhances ethanol metabolism in mice: Role of catalase: X. Chen, et al.; Free Radic. Biol. Med. 169, 283 (2021)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Ciglitazone | AG-CR1-0033 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioglitazone | AG-CR1-0067 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rosiglitazone . maleate | AG-CR1-3571 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||