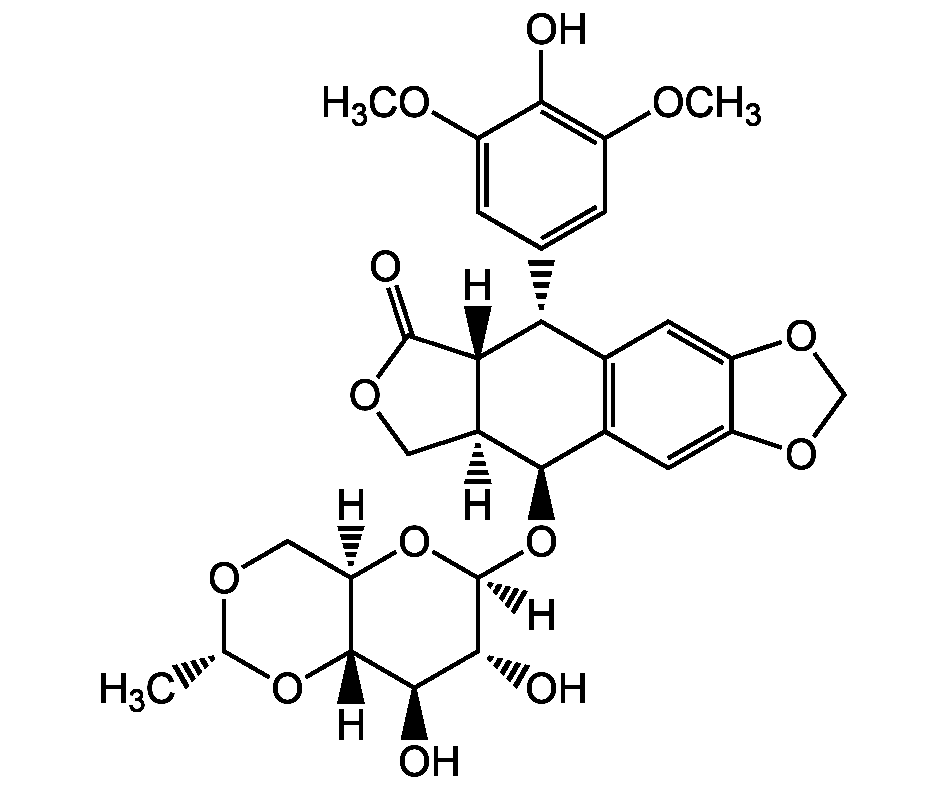
Etoposide
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3572-M025 | 25 mg | £40.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3572-M100 | 100 mg | £65.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3572-5100 | 5 x 100 mg | £230.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
+20°C
Storage:
+20deg;C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
VP-16-213; NSC 141540
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
33419-42-0
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07,GHS08
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H302, H350
InChi:
InChI=1S/C29H32O13/c1-11-36-9-20-27(40-11)24(31)25(32)29(41-20)42-26-14-7-17-16(38-10-39-17)6-13(14)21(22-15(26)8-37-28(22)33)12-4-18(34-2)23(30)19(5-12)35-3/h4-7,11,15,20-22,24-27,29-32H,8-10H2,1-3H3/t11-,15+,20-,21-,22+,24-,25-,26-,27-,29+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
VJJPUSNTGOMMGY-MRVIYFEKSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 33419-42-0. Formula: C29H32O13. MW: 588.6. Semisynthetic derivative of podophyllotoxin. Potent anti-cancer compound. Induces apoptosis in normal and tumor cell lines. DNA Topoisomerase II activity inhibitor. Increases Topo II-mediated DNA breakage primarily by inhibiting the ability of the enzyme to religate cleaved nucleic acid molecules. Does not lead to immediate block of DNS synthesis, induces a progressive inhibition of DNA replication. p53 activator. Blocks the cell cycle between the end of the S phase and the early G2 phase. Oncoprotein Mdm2 synthesis inhibitor. Apoptosis inducer through the cytochrome c/Apaf-1/caspase-9 pathway and the Fas-mediated death signaling pathway. Cell cycle checkpoint activator. Affects gene expression at different levels (chromatin remodeling, transcription and alternative splicing). Chemotherapeutic compound used in cancers. Used in conditioning regimen prior to a bone marrow or blood stem cell transplantation. Highly effective in mobilizing stem cells
MDL:
MFCD00869325
Molecular Formula:
C29H32O13
Molecular Weight:
588.6
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P301, P312, P308, P313, P330
Product Description:
Potent anti-cancer compound. Induces apoptosis in normal and tumor cell lines [1, 5]. DNA Topoisomerase II activity inhibitor. Increases Topo II-mediated DNA breakage primarily by inhibiting the ability of the enzyme to religate cleaved nucleic acid molecules. Does not lead to immediate block of DNS synthesis, induces a progressive inhibition of DNA replication [2, 4, 6]. p53 activator [3]. Blocks the cell cycle between the end of the S phase and the early G2 phase [2, 8]. Oncoprotein Mdm2 synthesis inhibitor [7]. Apoptosis inducer through the cytochrome c/Apaf-1/caspase-9 pathway and the Fas-mediated death signaling pathway [9, 10]. Cell cycle checkpoint activator. Affects gene expression at different levels (chromatin remodeling, transcription and alternative splicing) [11, 14, 15]. Chemotherapeutic compound used in cancers [12, 13]. Used in conditioning regimen prior to a bone marrow or blood stem cell transplantation [16]. Highly effective in mobilizing stem cells [17]
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Danger
SMILES:
[H][C@]12COC(=O)[C@]1([H])[C@H](C1=CC(OC)=C(O)C(OC)=C1)C1=C(C=C3OCOC3=C1)[C@H]2O[C@]1([H])O[C@]2([H])CO[C@@H](C)O[C@@]2([H])[C@H](O)[C@H]1O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol, methanol or dimethylformamide.
Source / Host:
Semisynthetic derivative of podophyllotoxin.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C. Store solutions in DMSO at 4°C. After reconstitution, prepare aliquots and store at -20°C.
References
The podophyllotoxin derivatives VP16-213 and VM26: B.F. Issell; Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 7, 73 (1982) | Topoisomerase-specific drug sensitivity in relation to cell cycle progression: K.C. Chow & W.E. Ross; Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 3119 (1987) | Increases in sequence specific DNA binding by p53 following treatment with chemotherapeutic and DNA damaging agents: R.B. Tishler, et al.; Cancer Res. 53, 2212 (1993) | Topoisomerase II-etoposide interactions direct the formation of drug-induced enzyme-DNA cleavage complexes: D.A. Burden, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 271, 29238 (1996) | Cell death induced by topoisomerase-targeted drugs: more questions than answers: S.H. Kaufmann; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1400, 195 (1998) (Review) | Etoposide: four decades of development of a topoisomerase II inhibitor: K.R. Hande; Eur. J. Cancer 34, 1514 (1998) (Review) | Differential regulation of p21waf-1/cip-1 and Mdm2 by etoposide: etoposide inhibits the p53-Mdm2 autoregulatory feedback loop: E.L. Arriola, et al.; Oncogene 18, 1081 (1999) | Early caspase activation in leukemic cells subject to etoposide-induced G2-M arrest: evidence of commitment to apoptosis rather than mitotic cell death: R.J. Sleiman & B.W. Stewart; Clin. Cancer Res. 6, 3756 (2000) | Ordering of ceramide formation, caspase activation, and Bax/Bcl-2 expression during etoposide-induced apoptosis in C6 glioma cells: M. Sawada, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 7, 761 (2000) | Distinct pathways for stimulation of cytochrome c release by etoposide: J.D. Robertson, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 275, 32438 (2000) | Deacetylase activity associates with topoisomerase II and is necessary for etoposide-induced apoptosis: C.A. Johnson, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 4539 (2001) | Etoposide: discovery and medicinal chemistry: P. Meresse, et al.; Curr. Med. Chem. 11, 2443 (2004) (Review) | Etoposide, topoisomerase II and cancer: E.L. Baldwin & N. Osheroff; Curr. Med. Chem. Anticancer Agents 5, 363 (2005) (Review) | The dispersal of replication proteins after Etoposide treatment requires the cooperation of Nbs1 with the ataxia telangiectasia Rad3-related/Chk1 pathway: R. Rossi, et al.; Cancer Res. 66, 1675 (2006) | Cellular response to etoposide treatment: A. Montecucco & G. Biamonti; Cancer Lett. 252, 9 (2007) (Review) | Chemomobilization with Etoposide is Highly Effective in Patients with Multiple Myeloma and Overcomes the Effects of Age and Prior Therapy: W.A. Wood, et al.; Biol. Blood Marrow. Transplant. 17, 141 (2011) | The aging effect of chemotherapy on cultured human mesenchymal stem cells. S. Buttiglieri, et al.; Exp. Hematol. 39, 1171 (2011)