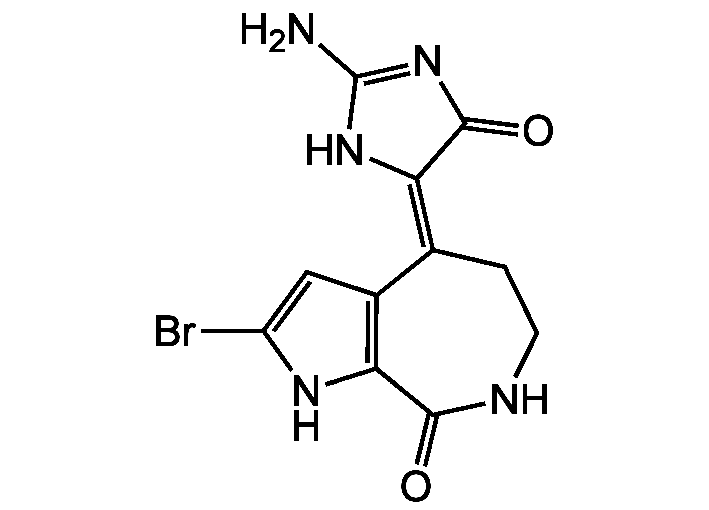
10Z-Hymenialdisine
Product Code: AG-CN2-0067
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0067-C500 | 500 ug | £210.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Hymenialdisine; 4-(2-Amino-4-oxo-2-imidazolidin-5-ylidene)-2-bromo-4,5,6,7-tetrahydropyrrolo[2,3-c]azepin-8-one
Appearance:
Light yellow solid.
CAS:
82005-12-7
Class:
6.1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS06
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Keep under inert gas.Protect from light.
Hazards:
H301, H311, H331
InChi:
InChI=1S/C11H10BrN5O2/c12-6-3-5-4(7-10(19)17-11(13)16-7)1-2-14-9(18)8(5)15-6/h3,15H,1-2H2,(H,14,18)(H3,13,16,17,19)/b7-4-
InChiKey:
ATBAETXFFCOZOY-DAXSKMNVSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 82005-12-7. Formula: C11H10BrN5O2. MW: 324.1. Isolated from sponge Axinella carteri. Insecticidal and cytotoxic. Potent NF-kappaB inhibitor. Inhibits various pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-alpha and nitric oxide (NO) in a variety of cell lines. ATP-competitive kinase inhibitor. Inhibits DNA damage checkpoint at G2, cyclin-dependent kinases CDK1/cyclin B, CDK2/cyclin A, CDK2/cyclin E, CDK4/cyclin D1, CDK5/p25, GSK-3beta and casein kinase 1 (CK1). Potent mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-1 (MEK-1) inhibitor. MARK (microtubule affinity-regulating kinase) inhibitor.
MDL:
MFCD04037007
Molecular Formula:
C11H10BrN5O2
Molecular Weight:
324.1
Package Type:
Vial
PG:
III
Precautions:
P261, P301, P310, P302, P352, P304, P340
Product Description:
Insecticidal and cytotoxic [1]. Potent NF-kappaB inhibitor. Inhibits various pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-alpha and nitric oxide (NO) in a variety of cell lines [2, 3, 4, 9]. ATP-competitive kinase inhibitor. Inhibits DNA damage checkpoint at G2, cyclin-dependent kinases CDK1/cyclin B, CDK2/cyclin A, CDK2/cyclin E, CDK4/cyclin D1, CDK5/p25, GSK-3beta and casein kinase 1 (CK1) [5, 6]. Potent mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-1 (MEK-1) inhibitor [7]. MARK (microtubule affinity-regulating kinase) inhibitor [8].
Purity:
>97% (HPLC) (Contains traces of the 10E-isomer)
Signal Word:
Danger
SMILES:
NC1=NC(=O)C(N1)=C1/CCNC(=O)C2=C1C=C(Br)N2
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO.
Source / Host:
Isolated from sponge Axinella carteri.
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
UN 2810
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Bioactive alkaloids from the tropical marine sponge Axinella carteri: A. Supriyono, et al.; Z. Naturforsch. [C] 50, 669 (1995) | The natural product hymenialdisine inhibits interleukin-8 production in U937 cells by inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB: J.J. Breton & M.C. Chabot-Fletcher; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 282, 459 (1997) | Inhibition of NFkappaB-mediated interleukin-1beta-stimulated prostaglandin E2 formation by the marine natural product hymenialdisine: A. Roshak, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 283, 955 (1997) | Inhibition of interleukin-1-induced proteoglycan degradation and nitric oxide production in bovine articular cartilage/chondrocyte cultures by the natural product, hymenialdisine: A.M. Badger, et al.; J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290, 587 (1999) | Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases, GSK-3beta and CK1 by hymenialdisine, a marine sponge constituent: L. Meijer, et al.; Chem. Biol. 7, 51 (2000) | Inhibition of the G2 DNA damage checkpoint and of protein kinases Chk1 and Chk2 by the marine sponge alkaloid debromohymenialdisine: D. Curman, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17914 (2001) | Aldisine alkaloids from the Philippine sponge Stylissa massa are potent inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-1 (MEK-1): D. Tasdemir, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 45, 529 (2002) | Protein kinase MARK/PAR-1 is required for neurite outgrowth and establishment of neuronal polarity: J. Biernat et al.; Mol. Biol. Cell. 13, 4013 (2002) | Inhibition of cytokine production by hymenialdisine derivatives: V. Sharma, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 47, 3700 (2004)