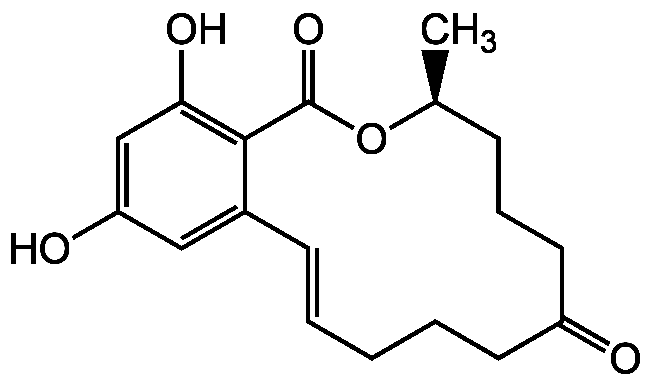
Zearalenone
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| BVT-0394-M005 | 5 mg | £80.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Toxin F2; BRN 1350216; FES; NCI-C50226; Zenone
Appearance:
Off-white solid.
CAS:
17924-92-4
Class:
8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS05,GHS08
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
Hazards:
H314, H361
InChi:
InChI=1S/C18H22O5/c1-12-6-5-9-14(19)8-4-2-3-7-13-10-15(20)11-16(21)17(13)18(22)23-12/h3,7,10-12,20-21H,2,4-6,8-9H2,1H3/b7-3+/t12-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
MBMQEIFVQACCCH-QBODLPLBSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 17924-92-4. Formula: C18H22O5. MW: 318.4. Isolated from Fusarium graminearum. Resorcylic acid lactone. Mycotoxin. Regulator of fungal morphogenesis. Mycoestrogen with anabolic and uterotrophic activity. Ecdysteroid antagonist. Gonadotropin inhibitor. Interleukin antagonist. Apoptosis inducer. Analytical standard in food industry.
MDL:
MFCD00133085
Molecular Formula:
C18H22O5
Molecular Weight:
318.4
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
PG:
III
Precautions:
P301, P330, P331, P303, P361, P353, P310
Product Description:
Resorcylic acid lactone. Mycotoxin. Regulator of fungal morphogenesis. Mycoestrogen with anabolic and uterotrophic activity. Ecdysteroid antagonist. Gonadotropin inhibitor. Interleukin antagonist. Apoptosis inducer. Analytical standard in food industry.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal Word:
Danger
SMILES:
C[C@H]1CCCC(=O)CCCC=CC2=CC(O)=CC(O)=C2C(=O)O1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, methanol or acetone.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Fusarium graminearum.
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
UN 1759
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 1 year after receipt when stored at -20°C. After reconstitution protect from light at -20°C.
References
The structure of zearalenone: W. H. Urry, et al.; Tetrahedron Lett. 1966, 3109 (1966) | Physicochemical data for some selected mycotoxins: A E. Pohland, et al.; Pure Appl. Chem. 54, 2219 (1982) | Zearalenone: K. Panneerselvam, et al.; Acta Cryst. C52, 3095 (1996) | The mycoestrogen zearalenone induces CYP3A through activation of the pregnane X receptor: X. Ding, et al.; Toxicol. Sci. 91, 448 (2006) | Trace mycotoxin analysis in complex biological and food matrices by liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure ionisation mass spectrometry: P. Zollner & B. Mayer-Helm; J. Chromatogr. A 1136, 123 (2006) | The PKS4 gene of Fusarium graminearum is essential for zearalenone production: E. Lysoe, et al; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 3924 (2006) | Chemistry and biology of resorcyclic acid lactones: N. Winssinger & S. Barluenga; Chem. Commun. 2007, 22 (2007) | Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: an oestrogenic mycotoxin: A. Zinedine, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 45, 1 (2007) | Biomimetic synthesis of resorcylate natural products utilizing late stage aromatization: concise total syntheses of the marine antifungal agents 15G256iota and 15G256beta: I. Navarro, et al.; JACS 130, 10293 (2008) | Effects of exposure to zearalenone on porcine oocytes and sperm during maturation and fertilization in vitro: R. Sambuu, et al.; J. Reprod. Dev. 57, 547 (2011) | Fusarium graminearum mycotoxins and their biosynthetic genes: H. Son & Y.-W. Lee; Mycotoxins 62, 29 (2012) | Zearalenone induces apoptosis and necrosis in porcine granulose cells via a caspase-3- and caspase-9-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway: L. Zhu, et al.; J. Cell. Physiol. 227, 1814 (2012)