RHAMM Antibody
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| PSI-6189-0.02mg | 0.02mg | £150.00 |
Quantity:
| PSI-6189-0.1mg | 0.1mg | £449.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Host Type: Rabbit
Antibody Isotype: IgG
Antibody Clonality: Polyclonal
Regulatory Status: RUO
Applications:
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
- Immunofluorescence (IF)
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
- Western Blot (WB)
Images
Documents
Further Information
Additional Names:
RHAMM Antibody: CD168, IHABP, RHAMM, Hyaluronan mediated motility receptor, Intracellular hyaluronic acid-binding protein
Application Note:
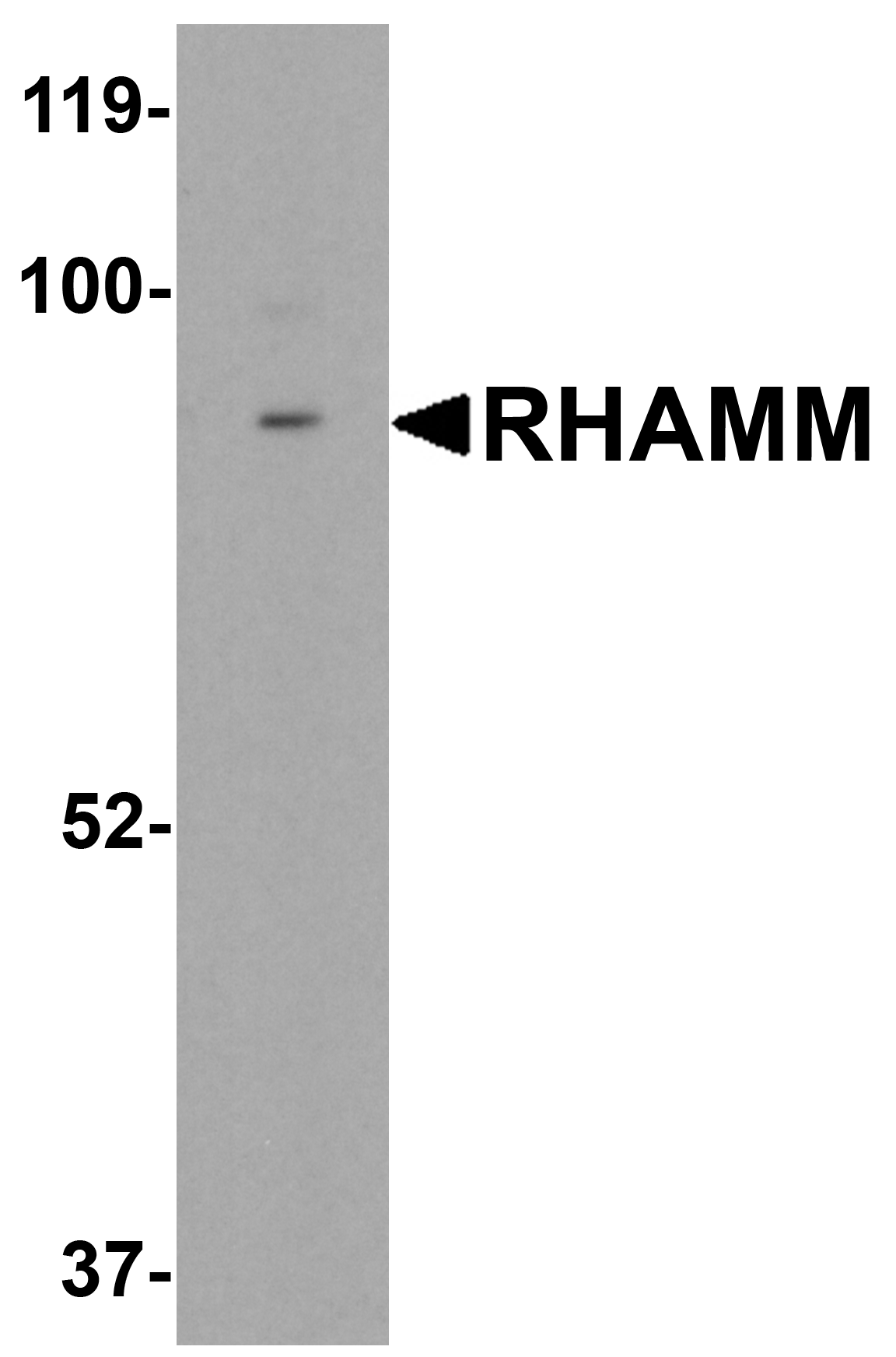
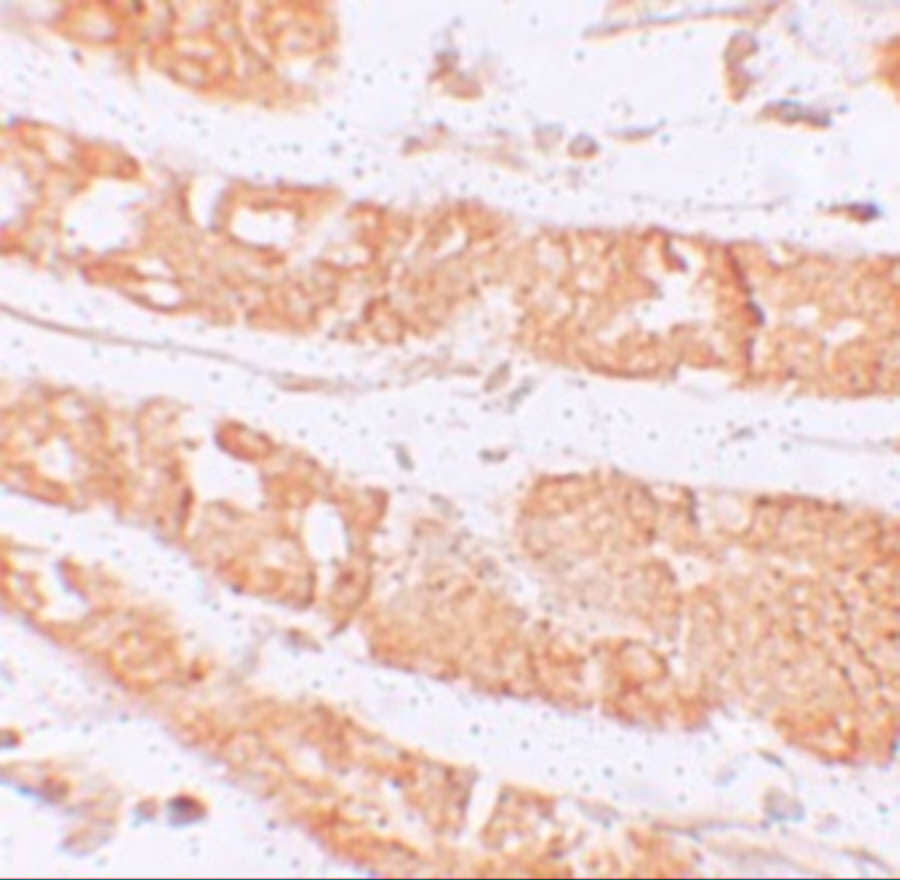
RHAMM antibody can be used for detection of RHAMM by Western blot at 0.5 μg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2.5 μg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 5 μg/mL.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in rat samples; Immunohistochemistry in human samples and Immunofluorescence in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Antibody validated: Western Blot in rat samples; Immunohistochemistry in human samples and Immunofluorescence in human samples. All other applications and species not yet tested.
Background:
RHAMM Antibody: The hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor, also known as RHAMM, was initially identified as a soluble protein that could be released by sub-confluent migrating cells, promoting cell motility and invasion via interactions with hyaluronan (HA) and the cell surface. While RHAMM is normally poorly expressed in most normal tissues and is not required for embryonic development or normal cell homeostasis functions, its expression is increased during wound repair in response to hypoxia and fibrogenic factors. However, its overexpression is transforming in multiple types of cancers and is required for maintaining RAS transformation. RHAMM associates with BRCA1 and BARD1, attenuating the mitotic-spindle-promoting activity of RHAMM, which may contribute to tumor progression by promoting genomic instability.
Background References:
- Hardwick C, Hoare K, Owens R, et al. Molecular cloning of a novel hyaluronan receptor that promotes tumor cell motility. J. Cell Biol. 1992; 117:1343-50.
- Samuel SK, Hurta RA, Spearman MA, et al. TGF-beta 1 stimulation of cell locomotion utilizes the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM and hyaluronan. J. Cell Biol. 1993; 123:749-58.
- Hall CL, Yang B, Yang X, et al. Overexpression of the hyaluronan receptor RHAMM is transforming and is also required for H-ras transformation. Cell 1995; 82:19-26.
- Maxwell CA, McCarthy J, and Turley E. Cell-surface and mitotic-spindle RHAMM: moonlighting or dual oncogenic functions J. Cell Sci. 2008; 121:925-32.
Buffer:
RHAMM Antibody is supplied in PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide.
Concentration:
1 mg/mL
Conjugate:
Unconjugated
DISCLAIMER:
Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. The information provided is a guideline for product use. This product is for research use only.
Immunogen:
RHAMM antibody was raised against a 18 amino acid synthetic peptide near the amino terminus of human RHAMM.
The immunogen is located within amino acids 80 - 130 of RHAMM.
The immunogen is located within amino acids 80 - 130 of RHAMM.
NCBI Gene ID #:
3161
NCBI Official Name:
yaluronan-mediated motility receptor
NCBI Official Symbol:
HMMR
NCBI Organism:
Homo sapiens
Physical State:
Liquid
Protein Accession #:
NP_036617
Protein GI Number:
217272802
Purification:
RHAMM Antibody is affinity chromatography purified via peptide column.
Research Area:
Cancer,Cell Cycle
Swissprot #:
O75330
User NOte:
Optimal dilutions for each application to be determined by the researcher.
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | RHAMM Peptide | PSI-6189P | ProSci | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|