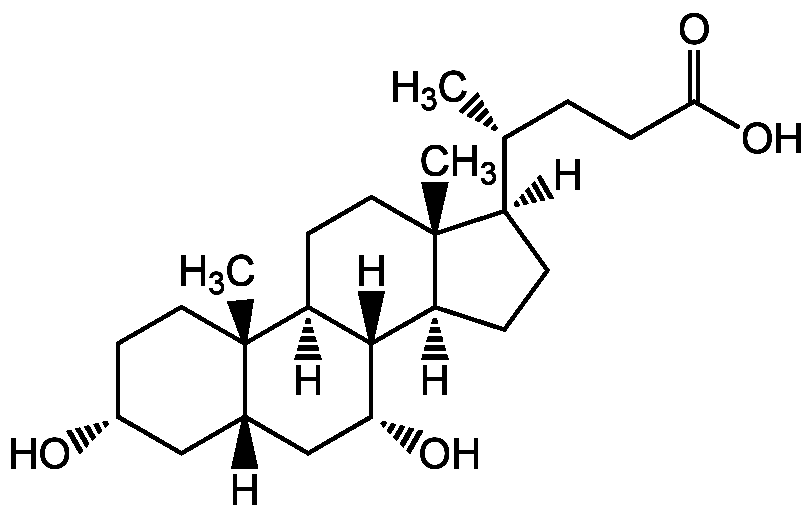
Chenodeoxycholic acid
Product Code: AG-CN2-0410
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0410-M100 | 100 mg | £30.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0410-M500 | 500 mg | £60.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
CDCA; Ulmenide; Kebilis; Hekbilin; Fluibil; Chenodiol; Anthropodeoxycholic acid
Appearance:
White to off-white crystalline powder.
CAS:
474-25-9
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light.Protect from moisture.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C24H40O4/c1-14(4-7-21(27)28)17-5-6-18-22-19(9-11-24(17,18)3)23(2)10-8-16(25)12-15(23)13-20(22)26/h14-20,22,25-26H,4-13H2,1-3H3,(H,27,28)/t14-,15+,16-,17-,18+,19+,20-,22+,23+,24-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
RUDATBOHQWOJDD-BSWAIDMHSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 474-25-9. Formula: C24H40O4. MW: 392.6. Synthetic. Originally isolated from bile. Cytotoxic hydrophobic primary bile acid. Activator of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor that is hepatoprotective and regulates bile acid synthesis (cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) suppression), conjugation and transport, as well as genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism and. Bile acid-controlled signaling pathways are promising novel targets to treat such metabolic diseases as obesity, type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. Inhibitor of 5beta-reductase (AKR1D1). Potent selective inhibitor of DD2 (AKR1C2). Potent inhibitor of 11beta-HSD1 dehydrogenase. Changes tumor cell viability via IL-6 pathway. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory compound. Modulates oxidative stress. Differentiation regulator of mouse embryonic stem cells. Used for dissolution of cholesterol gallstones.
MDL:
MFCD00064142
Molecular Formula:
C24H40O4
Molecular Weight:
392.6
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P264, P301, P312, P330
Product Description:
Cytotoxic hydrophobic primary bile acid [1]. Activator of farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor that is hepatoprotective and regulates bile acid synthesis (cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) suppression), conjugation and transport, as well as genes involved in lipid and glucose metabolism and [4-6, 14]. Bile acid-controlled signaling pathways are promising novel targets to treat such metabolic diseases as obesity, type II diabetes, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis [1, 8, 9, 12]. Inhibitor of 5beta-reductase (AKR1D1) [10, 15]. Potent selective inhibitor of DD2 (AKR1C2) [3]. Potent inhibitor of 11beta-HSD1 dehydrogenase [7]. Changes tumor cell viability via IL-6 pathway [11]. Anticancer compound. Apoptosis inducer [13]. Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory compound. Modulates oxidative stress [2, 16]. Differentiation regulator of mouse embryonic stem cells [17]. Used for dissolution of cholesterol gallstones.
Purity:
>95% (NMR)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])[C@H](O)C[C@]4([H])C[C@H](O)CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)[C@H](C)CCC(O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, ethanol or dimethylformamide. Sparingly soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic. Originally isolated from bile.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Bile acids as drugs: principles, mechanisms of action and formulations: A.F. Hofmann; Ital. J. Gastroenterol. 27, 106 (1995) (Review) | S-adenosil-L-methionine is able to reverse the immunosuppressive effects of chenodeoxycholic acid in vitro: G. Filaci, et al.; Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 19, 157 (1997) | Identification of amino acid residues responsible for differences in substrate specificity and inhibitor sensitivity between two human liver dihydrodiol dehydrogenase isoenzymes by site-directed mutagenesis: K. Matsuura, et al.; Biochem. J. 323, 61 (1997) | Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids: M. Makishima, et al.; Science 284, 1362 (1999) | Bile acids: natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor: D.J. Parks, et al.; Science 284, 1365 (1999) (Review) | A natural product that lowers cholesterol as an anatagonist ligand for FXR: N.L. Urizar, et al.; Science 296, 1703 (2002) | Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in various target tissues: D.J. Morris, et al.; Metabolism 53, 811 (2004) | The Farnesoid X Receptor - A Molecular Link Between Bile Acid and Lipid and Glucose Metabolism: T. Claudel, et al.; Hepatology 48, 1632 (2008) (Review) | Farnesoid X receptor antagonizes nuclear factor kappaB in hepatic inflammatory response: Y.D. Wang, et al.; Hepatology 48, 1632 (2008) (Review) | Bile acids modulate glucocorticoid metabolism and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in obstructive jaundice: A.D. McNeilly, et al.; J. Hepatol. 52, 705 (2010) | Effects of bile acids on expression of interleukin-6 and cell viability in QBC939 cell line: J. Wang, et al.; Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 48, 919 (2010) | Fasting plasma chenodeoxycholic acid and cholic acid concentrations are inversely correlated with insulin sensitivity in adults: B. Cariou, et al.; Nutrition & Metabolism 8, 48 (2011) | Deoxycholic and chenodeoxycholic bile acids induce apoptosis via oxidative stress in human colon adenocarcinoma cells: J.I. Barrasa, et al.; Apoptosis 16, 1054 (2011) | Farnesoid X receptor activation by chenodeoxycholic acid induces detoxifying enzymes through AMP-activated protein kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-mediated phosphorylation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta: K. Noh, et al.; Drug Metab. Dispos. 39, 1451 (2011) | Substrate specificity and inhibitor analyses of human steroid 5beta-reductase (AKR1D1): M. Chen, et al.; Steroids 76, 484 (2011) | Effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on fibrosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in kidney in high-fructose-fed Wistar rats: Z. Hu, et al.; Kidney Blood Press Res. 36, 85 (2012) | Direct effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells cultured under feeder-free culture conditions: S.J. Park, et al.; Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 375076 (2013)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Ursodeoxycholic acid | AG-CN2-0411 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|