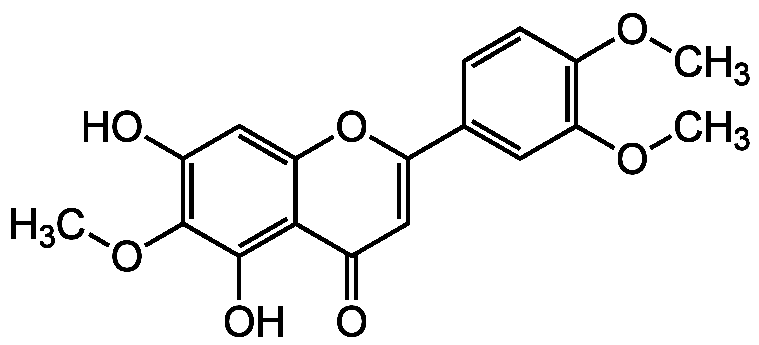
Eupatilin
Product Code: AG-CN2-0432
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0432-M005 | 5 mg | £60.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0432-M025 | 25 mg | £220.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
5,7-Dihydroxy-3',4',6-trimethoxyflavone; NSC 122413
Appearance:
Pale yellow powder.
CAS:
22368-21-4
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light.Protect from moisture.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C18H16O7/c1-22-12-5-4-9(6-14(12)23-2)13-7-10(19)16-15(25-13)8-11(20)18(24-3)17(16)21/h4-8,20-21H,1-3H3
InChiKey:
DRRWBCNQOKKKOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 22368-21-4. Formula: C18H16O7. MW: 344.3. Isolated from Artemisia sp. Selective inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase. Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest inducer. Anticancer compound. Inhibits ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-kappaB activation and expression of Raf-1 and Ras. Anti-proliferative compound. Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive. Anti-apoptotic compound in hepatocytes. Antioxidant. Antidiabetic. Enhances hepatic and plasma glucose metabolism and increases insulin secretion in type 2 diabetic mice. Inhibits angiogenesis by blocking STAT3 and VEGF expression. Neuroprotective. PI3K Class I, MKK3/6 and MKK4 inhibitor. Shown to inhibit osteoporosis dually through transcriptional suppression and actin rearrangement.
MDL:
MFCD13194819
Molecular Formula:
C18H16O7
Molecular Weight:
344.3
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P270, P301, P312, P330
Product Description:
Selective inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase. Anti-proliferative and anticancer compound. Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest inducer. Inhibits ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-kappaB activation and expression of Raf-1 and Ras. PI3K Class I, MKK3/6 and MKK4 inhibitor. Inhibits angiogenesis by blocking STAT3 and VEGF expression. Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive agent. Antioxidant. Antidiabetic. Enhances hepatic and plasma glucose metabolism and increases insulin secretion in type 2 diabetic mice. Selective PPARalpha agonist. Neuroprotective.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
COC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)O)OC)O)OC
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO, hot methanol or mixture of methanol and chloroform.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Artemisia sp.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Selective inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by natural compounds isolated from Chinese plants, Artemisia rubripes Nakai: Y. Koshihara, et al.; FEBS Lett. 158, 41 (1983) | Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia plants, induces apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia cells: H.J. Seo & Y.J. Surh; Mutat. Res. 496, 191-8 (2001) | Eupatilin, a pharmacologically active flavone derived from Artemisia plants, induces cell cycle arrest in ras-transformed human mammary epithelial cells: D.H. Kim, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 68, 1081 (2004) | Eupatilin blocks mediator release via tyrosine kinase inhibition in activated guinea pig lung mast cells: J.Y Kim, et al.; J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A. 68, 2063 (2005) | Eupatilin has an antiapoptotic action on hepatocytes, in contrast to apoptotic actions on other cells: T. Mine; J. Gastroenterol. 41, 818 (2006) | Eupatilin protects gastric epithelial cells from oxidative damage and down-regulates genes responsible for the cellular oxidative stress: E.J. Choi, et al.; Pharm. Res. 25, 1355 (2008) | Eupatilin inhibits H(2)O(2)-induced apoptotic cell death through inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB: S. Lee, et al.; Food Chem. Toxicol. 46, 2865 (2008) | Eupatilin, isolated from Artemisia princeps Pampanini, enhances hepatic glucose metabolism and pancreatic beta-cell function in type 2 diabetic mice: Y.J. Kang, et al.; Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 82, 25 (2008) | Eupatilin exhibits a novel anti-tumor activity through the induction of cell cycle arrest and differentiation of gastric carcinoma AGS cells: E.J. Choi, et al.; Differentiation 77, 412 (2009) | Eupatilin inhibits T-cell activation by modulation of intracellular calcium flux and NF-kappaB and NF-AT activity: Y.D. Kim, et al.; J. Cell Biochem. 108, 225 (2009) | Eupatilin Inhibits Gastric Cancer Cell Growth by Blocking STAT3-Mediated VEGF Expression: J.H. Cheong, et al.; J. Gastric Cancer 11, 16 (2011) | The neuroprotective effect of eupatilin against ischemia/reperfusion-induced delayed neuronal damage in mice: M. Cai, et al.; Eur. J. Pharmacol. 689, 104 (2012) | Eupatilin, a major flavonoid of Artemisia, attenuates aortic smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by inhibiting PI3K, MKK3/6, and MKK4 activities: J.E. Son, et al.; Planta Med. 79, 1009 (2013) | Massive elimination of multinucleated osteoclasts by eupatilin is due to dual inhibition of transcription and cytoskeletal rearrangement: J.-Y. Kim, et al.; Bone Rep. 3, 83 (2015) | Identification of eupatilin from Artemisia argyi as a selective PPARalpha agonist using affinity selection ultrafiltration LC-MS: Y. Choi, et al.; Molecules 20, 13753 (2015) | Eupatilin suppresses the allergic inflammatory response in vitro and in vivo: E-H. Song, et al.; Phytomed. 42, 1 (2018)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Ciglitazone | AG-CR1-0033 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioglitazone | AG-CR1-0067 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rosiglitazone | AG-CR1-3570 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rosiglitazone . maleate | AG-CR1-3571 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||