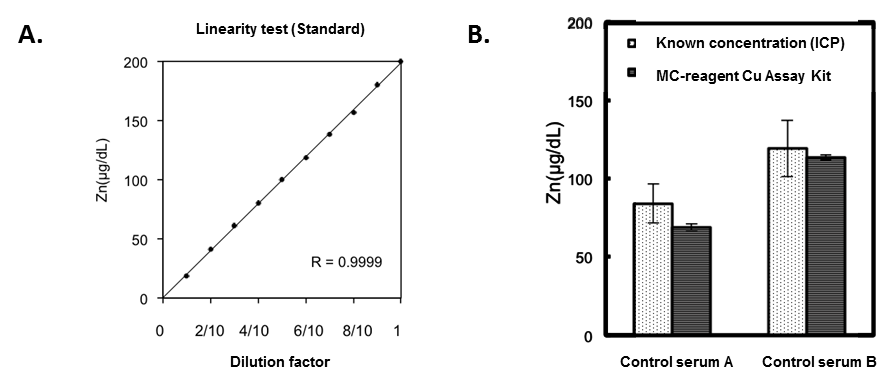Zinc Colorimetric Assay Kit
Product Code:
JAI-CZN-001
JAI-CZN-001
Regulatory Status:
RUO
RUO
Shipping:
BLUE ICE
BLUE ICE
Storage:
+4°C
+4°C
No additional charges, what you see is what you pay! *
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| JAI-CZN-001-100tests | 100 tests | £495.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Stay in control of your spending. These prices have no additional charges, not even shipping!
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
* Rare exceptions are clearly labelled (only 0.14% of items!).
Multibuy discounts available! Contact us to find what you can save.
This product comes from: Switzerland.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
Typical lead time: 10-14 working days.
Contact us for more accurate information.
- Further Information
- Documents
- References
- Related Products
- Show All
Further Information
Detection Type:
Colorimetric
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Do not freeze.
Kit Contains:
1 x 23 ml R-1 Buffer (ready to use) | 1 x 0.5 ml R-2 Chelate color (ready to use) | 1 x 1.2 ml STD Zinc (Zn) standard 200 µg/dL (ready to use)
Long Description:
This MC-Reagent Zinc Assay Kit is a direct colorimetric assay based on the 5-Br-PAPS method without deproteinization of the sample. The zinc determination is based on the reaction of zinc with 5-Br-PAPS at alkaline pH in a buffered media, which forms a stable colored complex. The color intensity is proportional to the zinc concentration in the sample. Absorbance of the Zn2+-complex is measured at 560nm. Wavelength range of sensitivity: 550 ~ 580nm. Features of this Assay: Quick & Easy to use • Species independent • Highly sensitive, stable and suitable for high-throughput testing • No toxic substances • For cell lysates, serum, plasma and wide variety of biological samples
Other data:
This MC-Reagent Zinc Assay Kit is a direct colorimetric assay based on the 5-Br-PAPS method without deproteinization of the sample. The zinc determination is based on the reaction of zinc with 5-Br-PAPS at alkaline pH in a buffered media, which forms a stable colored complex. The color intensity is proportional to the zinc concentration in the sample. Absorbance of the Zn2+-complex is measured at 560nm. Wavelength range of sensitivity: 550 ~ 580nm. Features of this Assay: Quick & Easy to use • Species independent • Highly sensitive, stable and suitable for high-throughput testing • No toxic substances • For cell lysates, serum, plasma and wide variety of biological samples
Package Type:
Box
Product Description:
Zinc (Zn2+) is an essential trace element, vital for the health of animals, plants, and microorganisms . Zinc is found in hundreds of enzymes, is stored and transferred in metallothioneins, and serves as structural ions in transcription factors. Zinc is often coordinated to the sides chains of amino acids, such as aspartic acid, glutamic acid, histidine and cysteine and is involved in nucleid acid and protein synthesis. It is therefore a necessary complement for cell replication. In humans, zinc interacts with a variety of organic ligands, and has roles in nucleic acid metabolism, apoptosis, neurological development, signal transduction, and gene expression. Zinc deficiency is related to skin lesions, irritability, loss of hair, growth retardation and impaired immunological functions.
Range:
4 - 1000µg/dL
Sample Type:
Cell Lysate, Plasma, Saliva, Serum, Tissue Supernatant, Urine
Specificity:
Specific to Zn2+.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Chemical Reagent Kits
UNSPSC Number:
41116104
Use & Stability:
12 months after the day of manufacturing. See expiry date on ELISA Kit box.
Documents
References
The therapeutic effect on bone mineral formation from biomimetic zinc containing tricalcium phosphate (ZnTCP) in zinc-deficient osteoporotic mice: J. Chou, et al.; PLoS One 8, e71821 (2013) | A Primary Role for Disulfide Formation in the Productive Folding of Prokaryotic Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase: Y. Sakurai, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 289, 20139 (2014)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Calcium Colorimetric Assay Kit (Chlorophosphonazo III Method)) | JAI-CCA-020 | JaICA | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium Colorimetric Assay Kit (o-Cresolphthalein-Complexone Method) | JAI-CCA-030 | JaICA | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Copper Colorimetric Assay Kit | JAI-CCU-400 | JaICA | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Iron Colorimetric Assay Kit (Nitroso-PSAP Method) | JAI-CFE-010 | JaICA | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnesium Colorimetric Assay Kit (Yyridil Blue-I Method) | JAI-CMG-035 | JaICA | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Antioxidant Capacity (PAO) Test Kit | JAI-KPA-050 | JaICA | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||