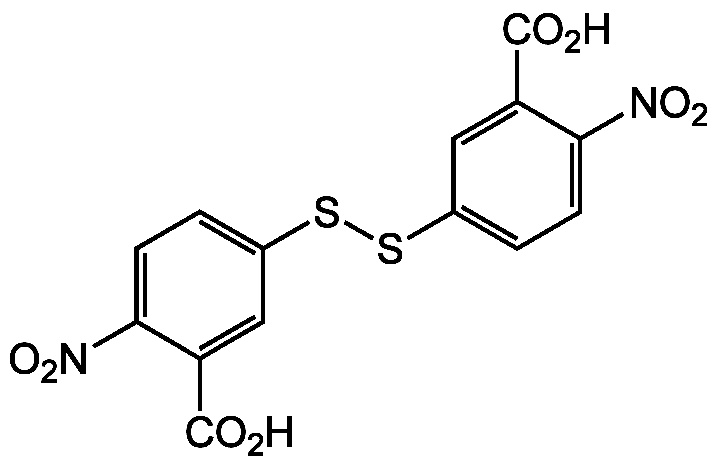
DTNB
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-D0156-G001 | 1 g | £41.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-D0156-G005 | 5 g | £78.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-D0156-G025 | 25 g | £164.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Ellman's Reagent; 5,5'-Dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid)
Appearance:
Yellow powder.
CAS:
69-78-3
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H315, H319, H335
InChi:
InChI=1S/C14H8N2O8S2/c17-13(18)9-5-7(1-3-11(9)15(21)22)25-26-8-2-4-12(16(23)24)10(6-8)14(19)20/h1-6H,(H,17,18)(H,19,20)
InChiKey:
KIUMMUBSPKGMOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 69-78-3. Formula: C14H8N2O8S2. MW: 396.35. Synthetic A sensitive reagent for measuring the free sulfhydryl content in proteins, peptides, and tissues. Used to characterize reactive thiol groups and photometric determination of thiols and for measuring low-molecular mass thiols such as glutathione in both pure solutions and biological samples, such as blood. It can also measure the number of thiol groups on proteins. Through reaction with aliphatic thiol groups a mixed disulfide of protein thiol and one mole of 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoate per mole of protein sulfhydryl group is being formed. DTNB has little absorbance. Reaction with -SH groups on proteins (from any solvent accessible Cys) under mild alkaline conditions (pH 7-8) produces the 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoate anion, which gives an intense yellow color with an absorption maximum at 409.5nm (Extinction coefficient: 14150 M-1*cm-1). Sensitive to various buffer ions, therefore, the extinction coefficient used to calculate the number of sulfhydryl groups must be matched to the reaction conditions. In case the thiol groups are in disulfide bonds, they must be reduced under anaerobic conditions prior to reaction with DTNB.
MDL:
MFCD00007140
Molecular Formula:
C14H8N2O8S2
Molecular Weight:
396.35
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P305, P351, P338
Product Description:
A sensitive reagent for measuring the free sulfhydryl content in proteins, peptides, and tissues. Used to characterize reactive thiol groups and photometric determination of thiols and for measuring low-molecular mass thiols such as glutathione in both pure solutions and biological samples, such as blood. It can also measure the number of thiol groups on proteins. Through reaction with aliphatic thiol groups a mixed disulfide of protein thiol and one mole of 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoate per mole of protein sulfhydryl group is being formed. DTNB has little absorbance. Reaction with -SH groups on proteins (from any solvent accessible Cys) under mild alkaline conditions (pH 7-8) produces the 2-nitro-5-thiobenzoate anion, which gives an intense yellow color with an absorption maximum at 409.5nm (Extinction coefficient: 14150 M-1*cm-1). Sensitive to various buffer ions, therefore, the extinction coefficient used to calculate the number of sulfhydryl groups must be matched to the reaction conditions. In case the thiol groups are in disulfide bonds, they must be reduced under anaerobic conditions prior to reaction with DTNB.
Purity:
>98% (Titration)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
OC(=O)C1=CC(SSC2=CC=C(C(=C2)C(O)=O)[N+]([O-])=O)=CC=C1[N+]([O-])=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in ethanol, dioxane or phosphate buffer.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C.
References
(1) G.L. Ellman; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 82, 70 (1959) | (2) H.B. Collier; Anal. Biochem. 56, 310 (1973) | (3) P.W. Riddles, et al.; Meth. Enzymol. 91, 49 (1983) | (4) C.K. Riener, et al.; Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 373, 266 (2002) | (5) J. Sedlak & R.H. Lindsay; Anal. Biochem. 25, 192 (1968) | (6) G.L. Ellman; Biochem. Pharmacol. 7, 88 (1961) | (7) M.J. Gething & B.E. Davidson; Eur. J. Biochem. 30, 352 (1972) | (8) A.F.S.A. Habeeb; Meth. Enzymol. 25, 457 (1972) | (9) D. Ming, et al.; Biotechniques 18, 808 (1995)