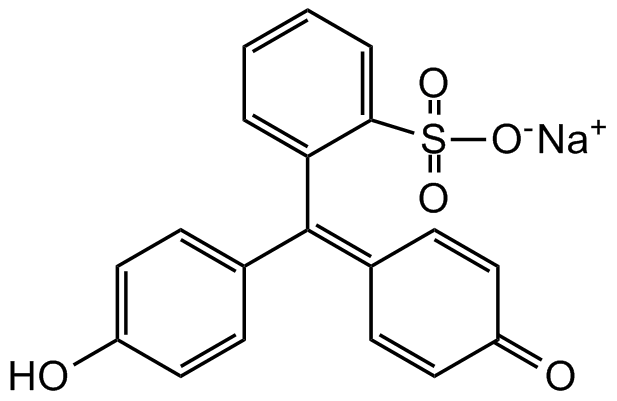
Phenol red sodium salt
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-P0026-G001 | 1 g | £35.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-P0026-G010 | 10 g | £78.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-P0026-G050 | 50 g | £212.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
4,4'-(1,1-Dioxido-3H-2,1-benzoxathiol-3-ylidene)bis-phenol sodium salt
Appearance:
Dark red powder.
CAS:
34487-61-1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H315, H319, H335
InChi:
InChI=1S/C19H14O5S.Na/c20-15-9-5-13(6-10-15)19(14-7-11-16(21)12-8-14)17-3-1-2-4-18(17)25(22,23)24;/h1-12,20H,(H,22,23,24);/q;+1/p-1
InChiKey:
RBFZWTMVVUVHLM-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 34487-61-1. Formula: C19H13O5S . Na. MW: 376.36. Synthetic Water soluble pH indicator used in the 6.8 (yellow) to 8.2 (red) range and frequently used in cell biology laboratories. Widely used as cell tissue culture pH marker. A small amount of phenol red added to the growth medium will have a pink-red color under normal conditions. Typically, 15 mg/l are used for cell culture. In the event of problems, waste products produced by dying cells or overgrowth of contaminants will cause a change in pH, leading to a change in indicator color. For example, a culture of relatively slowly dividing mammalian cells can be quickly overgrown by bacterial contamination. This usually results in an acidification of the medium, turning it yellow. The waste products produced by the mammalian cells themselves will slowly decrease the pH, gradually turning the solution orange and then yellow. This color change is an indication that even in the absence of contamination, the medium needs to be replaced. Shown to be a weak estrogen mimic (possible through inpurities), which can enhance the growth of cells that express the estrogen receptor in cell cultures. Might be useful as a differentiation factor.
MDL:
MFCD00066901
Molecular Formula:
C19H13O5S . Na
Molecular Weight:
376.36
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P305, P351, P338
Product Description:
Water soluble pH indicator used in the 6.8 (yellow) to 8.2 (red) range and frequently used in cell biology laboratories. Widely used as cell tissue culture pH marker. A small amount of phenol red added to the growth medium will have a pink-red color under normal conditions. Typically, 15 mg/l are used for cell culture. In the event of problems, waste products produced by dying cells or overgrowth of contaminants will cause a change in pH, leading to a change in indicator color. For example, a culture of relatively slowly dividing mammalian cells can be quickly overgrown by bacterial contamination. This usually results in an acidification of the medium, turning it yellow. The waste products produced by the mammalian cells themselves will slowly decrease the pH, gradually turning the solution orange and then yellow. This color change is an indication that even in the absence of contamination, the medium needs to be replaced. Shown to be a weak estrogen mimic (possible through inpurities), which can enhance the growth of cells that express the estrogen receptor in cell cultures. Might be useful as a differentiation factor.
Purity:
Dye content 90 % (Titration)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
[Na+].OC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=C1C=CC(=O)C=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1S([O-])(=O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C.
References
(1) F.L. Rodkey; Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 94, 38 (1961) | (2) T. Hoshi & H. Hayashi; Jpn. J. Physiol. 20, 683 (1970) | (3) U. Kragh-Hansen & J.V. Moller; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 295, 438 (1973) | (4) Y. Berthois, et al.; PNAS 83, 2496 (1986) | (5) P. Yuan & D.R. Walt; J. Fluoresc. 2, 231 (1992) | (6) L. Hopp & C.H. Bunker; J. Cell Physiol. 157, 594 (1993) | (7) J. Wesierska-Gadek, et al.; Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 12, 280 (2007) | (8) H. Lysdahl, et al.; Stem Cell Rev. 9, 132 (2013)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | DCFA | CDX-C0043 | Chemodex | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHPDS | CDX-D0078 | Chemodex | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fluorescein octadecyl ester | CDX-F0074 | Chemodex | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HPTS | CDX-H0034 | Chemodex | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8-Hydroxy-N,N,N',N',N'',N''-hexamethyl-pyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonamide | CDX-H0043 | Chemodex | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,3,6,8-Pyrenetetrasulfonic acid tetrasodium salt | CDX-P0021 | Chemodex | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SNARF-DE | CDX-S0037 | Chemodex | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||