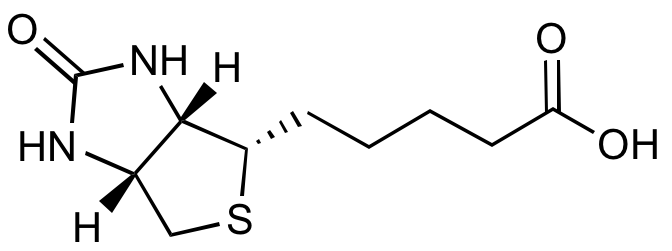
D-Biotin
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-B0148-G001 | 1 g | £59.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-B0148-G005 | 5 g | £145.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-B0148-G025 | 25 g | £560.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Bios II; Biotin; Coenzyme R; Vitamin B7; Vitamin H; NSC 63865; Factor S
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
58-85-5
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C10H16N2O3S/c13-8(14)4-2-1-3-7-9-6(5-16-7)11-10(15)12-9/h6-7,9H,1-5H2,(H,13,14)(H2,11,12,15)/t6-,7-,9-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
YBJHBAHKTGYVGT-ZKWXMUAHSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 58-85-5. Formula: C10H16N2O3S. MW: 244.3. Synthetic. D-(+)-Biotin, also known as vitamin H or coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-vitamin (vitamin B7). D-(+)-Biotin is a cofactor responsible for carbon dioxide transfer in five carboxylase enzymes, such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha, acetyl-CoA carboxylase beta, methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase, propionyl-CoA carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase. It is important in fatty acid synthesis, branched-chain amino acid catabolism and gluconeogenesis. It covalently attaches to the epsilon-amino group of specific lysine residues in these carboxylases. This biotinylation reaction requires ATP and is catalyzed by holocarboxylase synthetase. Biotin is also covalently attached to distinct lysine residues in histones, affecting chromatin structure and mediating gene regulation. Biotin is widely used throughout the biotechnology industry to conjugate proteins for biochemical assays. Biotin's small size means the biological activity of the protein will most likely be unaffected. This process is called biotinylation. Because both streptavidin and avidin bind biotin with high affinity (Kd of 10-14 mol/l to 10-15 mol/l) and specificity, biotinylated proteins of interest can be isolated from a sample by exploiting this highly stable interaction. The sample is incubated with streptavidin/avidin beads, allowing capture of the biotinylated protein of interest. The attachment of biotin to various chemical sites is used to study various processes, including protein localization, protein interactions, DNA transcription and replication.
MDL:
MFCD00005541
Molecular Formula:
C10H16N2O3S
Molecular Weight:
244.3
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
D-(+)-Biotin, also known as vitamin H or coenzyme R, is a water-soluble B-vitamin (vitamin B7). D-(+)-Biotin is a cofactor responsible for carbon dioxide transfer in five carboxylase enzymes, such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha, acetyl-CoA carboxylase beta, methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase, propionyl-CoA carboxylase or pyruvate carboxylase. It is important in fatty acid synthesis, branched-chain amino acid catabolism and gluconeogenesis. It covalently attaches to the epsilon-amino group of specific lysine residues in these carboxylases. This biotinylation reaction requires ATP and is catalyzed by holocarboxylase synthetase. Biotin is also covalently attached to distinct lysine residues in histones, affecting chromatin structure and mediating gene regulation. Biotin is widely used throughout the biotechnology industry to conjugate proteins for biochemical assays. Biotin's small size means the biological activity of the protein will most likely be unaffected. This process is called biotinylation. Because both streptavidin and avidin bind biotin with high affinity (Kd of 10-14 mol/l to 10-15 mol/l) and specificity, biotinylated proteins of interest can be isolated from a sample by exploiting this highly stable interaction. The sample is incubated with streptavidin/avidin beads, allowing capture of the biotinylated protein of interest. The attachment of biotin to various chemical sites is used to study various processes, including protein localization, protein interactions, DNA transcription and replication.
Purity:
>98% (NMR)
SMILES:
[H][C@]12CS[C@@H](CCCCC(O)=O)[C@@]1([H])NC(=O)N2
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in hot water or DMSO (49mg/ml at 25°C).
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Fluorescent Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
41105331
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
(1) A. Chapman-Smith & J.E. Cronan Jr.; J. Nutr. 129, 477S (1999) | (2) J. Zempleni & D.M. Mock; J. Nutr. Biochem. 10, 128 (1999) | (3) A. Holmberg, et al.; Electrophoresis 26, 501 (2005) | (4) J. Zempleni, et al.; Biofactors 35, 36 (2009)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | N-(2-Aminoethyl)biotinamide hydrochloride | CDX-A0191 | Chemodex | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biotin-(5-fluorescein)-conjugate | CDX-B0078 | Chemodex | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biotinyl tyramide | CDX-B0270 | Chemodex | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||