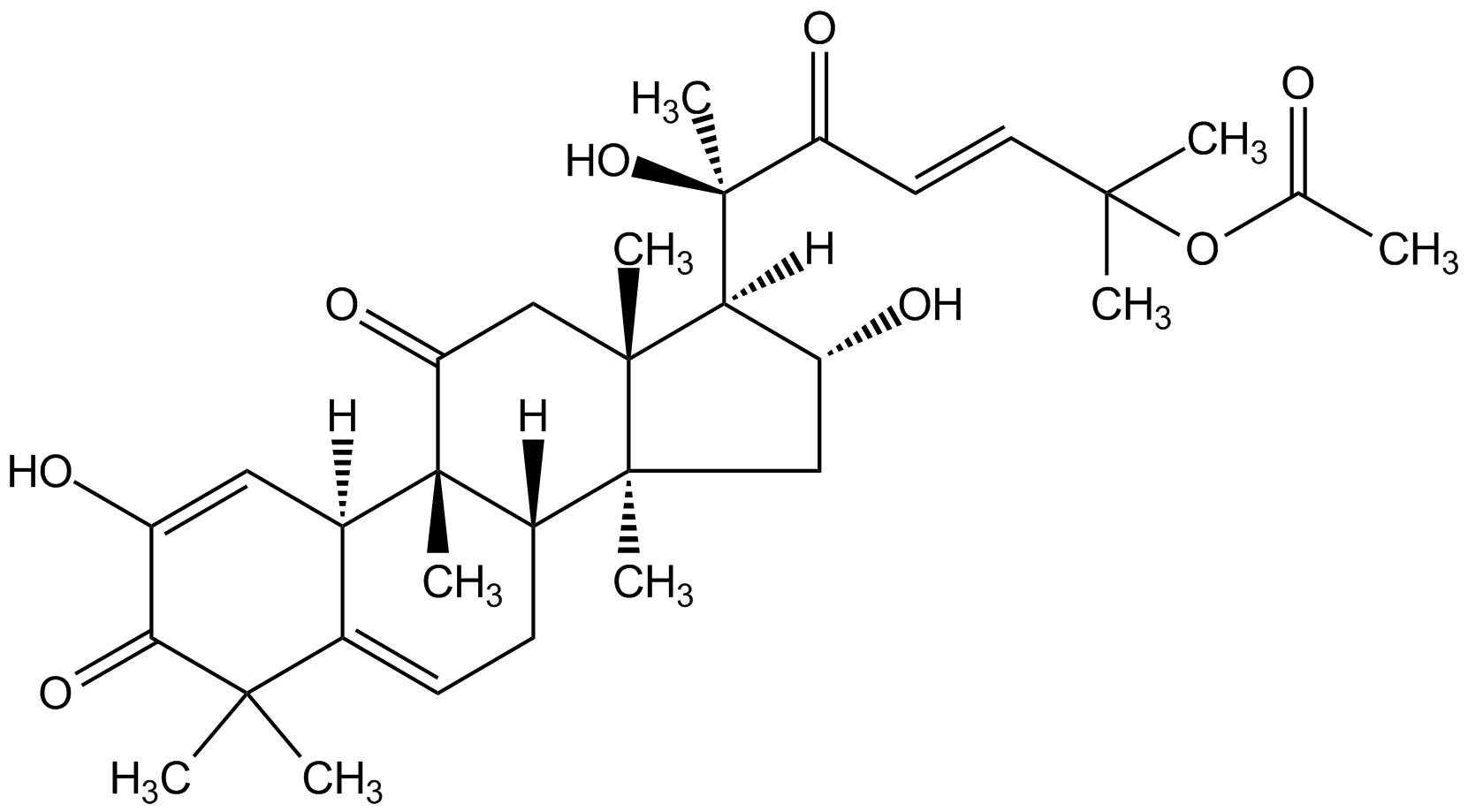
Cucurbitacin E
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0474-M001 | 1 mg | £40.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0474-M005 | 5 mg | £120.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CN2-0474-M025 | 25 mg | £450.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
Short term: +4°C, Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Cuc E; alpha-Elaterin; alpha-Elaterine; NSC106399; BRN2343323
Appearance:
Off-white powder.
CAS:
18444-66-1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C32H44O8/c1-17(33)40-27(2,3)13-12-23(36)32(9,39)25-21(35)15-29(6)22-11-10-18-19(14-20(34)26(38)28(18,4)5)31(22,8)24(37)16-30(25,29)7/h10,12-14,19,21-22,25,34-35,39H,11,15-16H2,1-9H3/b13-12+/t19-,21-,22+,25+,29+,30-,31+,32+/m1/s1
InChiKey:
NDYMQXYDSVBNLL-MUYMLXPFSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 18444-66-1. Formula: C32H44O8. MW: 556.7. Isolated from Cucumis melo L. Potent actin depolymerization inhibitor. Shown to have a different mechanism of action compared to jasplakinolide (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0037), binding to a different site. Binds specifically to filamentous actin (F-actin) forming a covalent bond at residue Cys257, stabilizing F-actin without affecting actin polymerization or nucleation. Does not bind to monomeric actin (G-actin). Immunomodulator with anti-inflammatory and anti-tumorigenic properties in a range of cancer cell lines, mediated by its action on the cellular cytoskeleton, on mitotic pathways as well as on cellular autophagy. Shown to induce apoptosis, autophagy and cell cycle arrest at G2/M. Inhibits tumor angiogenesis through Jak-STAT3 signaling pathway, suppresses cell migration and invasion, and inhibits NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. Antioxidant and potential neuroprotective compound with potential neurodegenerative properties.
MDL:
MFCD00135936
Molecular Formula:
C32H44O8
Molecular Weight:
556.7
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P270, P301, P312, P330
Product Description:
Potent actin depolymerization inhibitor. Shown to have a different mechanism of action compared to jasplakinolide (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0037), binding to a different site. Binds specifically to filamentous actin (F-actin) forming a covalent bond at residue Cys257, stabilizing F-actin without affecting actin polymerization or nucleation. Does not bind to monomeric actin (G-actin). Immunomodulator with anti-inflammatory and anti-tumorigenic properties in a range of cancer cell lines, mediated by its action on the cellular cytoskeleton, on mitotic pathways as well as on cellular autophagy. Shown to induce apoptosis, autophagy and cell cycle arrest at G2/M. Inhibits tumor angiogenesis through Jak-STAT3 signaling pathway, suppresses cell migration and invasion, and inhibits NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. Antioxidant and potential neuroprotective compound with potential neurodegenerative properties.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
[H][C@@]1([C@H](O)C[C@@]2(C)[C@]3([H])CC=C4[C@@]([H])(C=C(O)C(=O)C4(C)C)[C@]3(C)C(=O)C[C@]12C)[C@@](C)(O)C(=O)C=CC(C)(C)OC(C)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Cucumis melo L.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352211
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Cucurbitacin E-induced disruption of the actin and vimentin cytoskeleton in prostate carcinoma cells: K.L. Duncan, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 52, 1553 (1996) | Cucurbitacin glucosides: antioxidant and free-radical scavenging activities: T. Tannin-Spitz, et al.; BBRC 364, 181 (2007) | Direct interaction of Cucurbitacin E isolated from Alsomitra macrocarpa to actin filament: K. Momma, et al.; Cytotechnology 56, 33 (2008) | Cucurbitacin E, a tetracyclic triterpenes compound from Chinese medicine, inhibits tumor angiogenesis through VEGFR2-mediated Jak2-STAT3 signaling pathway: Y. Dong, et al.; Carcinogenesis 31, 2097 (2010) | Cucurbitacin E Induces G(2)/M Phase Arrest through STAT3/p53/p21 Signaling and Provokes Apoptosis via Fas/CD95 and Mitochondria-Dependent Pathways in Human Bladder Cancer T24 Cells: W.W. Huang, et al.; Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2012, 952762 (2012) | The natural product cucurbitacin E inhibits depolymerization of actin filaments: P.M. Soerensen, et al.; ACS Chem. Biol. 7, 1502 (2012) | Cucurbitacin E inhibits breast tumor metastasis by suppressing cell migration and invasion: T. Zhang, et al.; Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 135, 445 (2012) | Cucurbitacin E exhibits anti-inflammatory effect in RAW 264.7 cells via suppression of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation: J. Qiao, et al.; Inflamm. Res. 62, 461 (2013) | Cucurbitacin E as inducer of cell death and apoptosis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line SAS: C.M. Hung, et al.; Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 17147 (2013) | Cucurbitacin E has neuroprotective properties and autophagic modulating activities on dopaminergic neurons: A.M. Arel-Dubeau, et al.; Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 425496 (2014) | Inducement of mitosis delay by cucurbitacin E, a novel tetracyclic triterpene from climbing stem of Cucumis melo L. through GADD45gamma in human brain malignant glioma (GBM) 8401 cells: Y.C. Hsu, et al.; Cell Death Dis. 5, e1087 (2014) | Cucurbitacin E Induces Autophagy via Downregulating mTORC1 Signaling and Upregulating AMPK Activity: Q.B. Zha, et al.; PLoS One 10, e0124355 (2015)