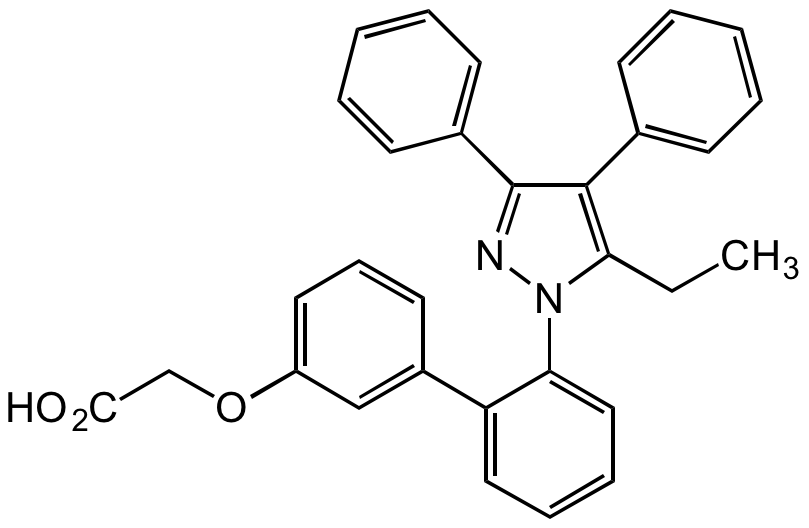
BMS-309403
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3640-M001 | 1 mg | £40.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3640-M005 | 5 mg | £75.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3640-M025 | 25 mg | £270.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
-20°C
Storage:
Short Term: 4°C Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
BMS309403; BMS 309403; FABP4 Inhibitor; 2-[[2'-(5-Ethyl-3,4-diphenyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl)[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-yl]oxy]acetic acid
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
300657-03-8
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C31H26N2O3/c1-2-27-30(22-12-5-3-6-13-22)31(23-14-7-4-8-15-23)32-33(27)28-19-10-9-18-26(28)24-16-11-17-25(20-24)36-21-29(34)35/h3-20H,2,21H2,1H3,(H,34,35)
InChiKey:
SJRVJRYZAQYCEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 300657-03-8. Formula: C31H26N2O3. MW: 474.6. Cell permeable, potent and selective fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4; A-FABP; ALBP; adipocyteP2 protein) inhibitor that competitively targets the fatty acid-binding pocket (Ki= <2nM). Inhibits FABP3 (muscle) and FABP5 (epidermal) with lower affinity (Ki=250nM and 350nM, respectively). FABP4 is an intracellular lipid-binding protein responsible for the transportation of fatty acids. It is expressed primarily in adipose tissue and is associated with inflammation, obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Glucose uptake stimulator. Reduces blood glucose levels and increases insulin sensitivity in a mouse model of obesity. Protects against the development of insulin resistance associated with genetic or diet-induced obesity in mice. Anti-atherosclerotic. Decreases fatty acid uptake in adipocytes in vitro and reduces atherosclerotic lesion area in a mouse model of atherosclerosis.
MDL:
MFCD09991687
Molecular Formula:
C31H26N2O3
Molecular Weight:
474.6
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
Cell permeable, potent and selective fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4; A-FABP; ALBP; adipocyteP2 protein) inhibitor that competitively targets the fatty acid-binding pocket (Ki= <2nM). Inhibits FABP3 (muscle) and FABP5 (epidermal) with lower affinity (Ki=250nM and 350nM, respectively). FABP4 is an intracellular lipid-binding protein responsible for the transportation of fatty acids. It is expressed primarily in adipose tissue and is associated with inflammation, obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Glucose uptake stimulator. Reduces blood glucose levels and increases insulin sensitivity in a mouse model of obesity. Protects against the development of insulin resistance associated with genetic or diet-induced obesity in mice. Anti-atherosclerotic. Decreases fatty acid uptake in adipocytes in vitro and reduces atherosclerotic lesion area in a mouse model of atherosclerosis.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
SMILES:
CCC1=C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)=NN1C4=CC=CC=C4C5=CC(OCC(O)=O)=CC=C5
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml), ethanol (30mg/ml), dimethylformamide (30mg/ml) or methanol. Almost insoluble in water.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Potent and selective biphenyl azole inhibitors of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (aFABP): R. Sulsky, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 17, 3511 (2007) | Treatment of diabetes and atherosclerosis by inhibiting fatty-acid-binding protein aP2: M. Furuhashi, et al.; Nature 447, 959 (2007) | BMS309403 stimulates glucose uptake in myotubes through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase: W. Lin, et al.; PLoS One 7, e44570 (2012) | FABP4 attenuates PPARgamma and adipogenesis and is inversely correlated with PPARgamma in adipose tissues: T. Garin-Shkolnik, et al.; Diabetes 63, 900 (2014) | FABP4 inhibition suppresses PPARgamma activity and VLDL-induced foam cell formation in IL-4-polarized human macrophages: M. Boss, et al.; Atherosclerosis 240, 424 (2015)