Indo 1-AM
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-I0019-M001 | 1 mg | £157.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
Short Term: -20°C . Long Term: -20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
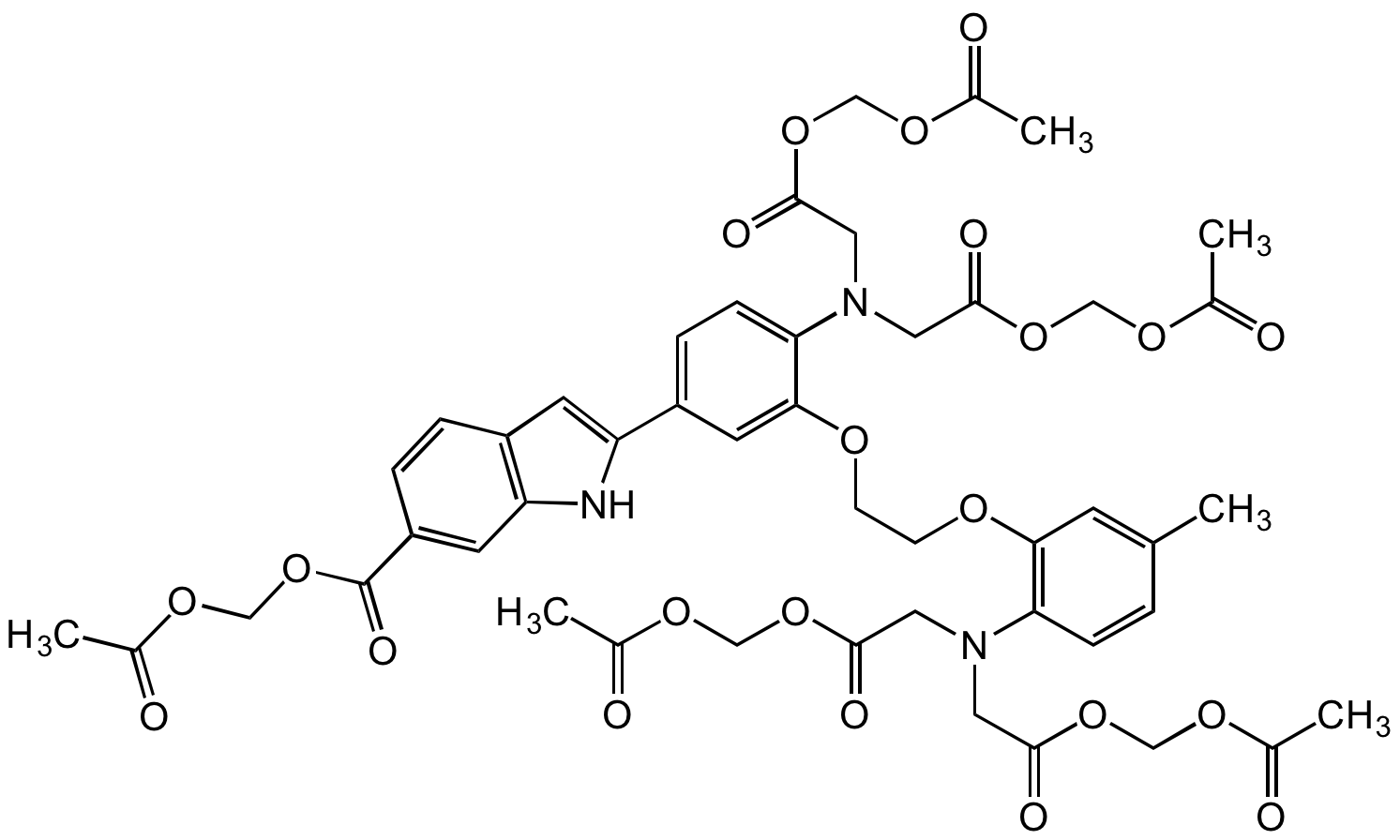
Indo-1-(acetoxymethyl) ester; 4-(6-Carboxy-2-indolyl)-4'-methyl-2,2'-(ethylenedioxy)dianiline-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid tetrakis(acetoxymethyl) ester
Appearance:
Off-white solid.
CAS:
112926-02-0
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light and moisture.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C47H51N3O22/c1-28-7-11-39(49(19-43(56)68-23-63-29(2)51)20-44(57)69-24-64-30(3)52)41(15-28)61-13-14-62-42-18-35(37-16-34-8-9-36(17-38(34)48-37)47(60)72-27-67-33(6)55)10-12-40(42)50(21-45(58)70-25-65-31(4)53)22-46(59)71-26-66-32(5)54/h7-12,15-18,48H,13-14,19-27H2,1-6H3
InChiKey:
CAWBRCOBJNWRLK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 112926-02-0. Formula: C47H51N3O22. MW: 1009.93. Synthetic. INDO 1-AM is a popular non-invasive UV-excitable calcium indicator. It is the cell-permeable ester derivative of INDO 1. After crossing the cell membrane, INDO 1-AM is rapidly hydrolyzed by cytoplasmic esterases to produce the ratiometric fluorescent calcium indicator INDO 1, which remains trapped within the cell. INDO 1/AM has been used to selectively monitor Ca2+ levels in mitochondria and in the cytosol. INDO 1 is ideal for analyses using flow cytometry, as it uses a single excitation source (usually the 351-364nm spectral lines of the argon-ion laser). In contrast to FURA 1, INDO 1 has a dual emission peak. The emission of INDO 1 shifts to 400nm (when bound to Ca2+) from 480nm in Ca2+-free environments. INDO 1 is prone to photobleaching, which limits its usefulness in methods involving microscopy. Calcium measurement is critical for numerous biological investigations. Fluorescent probes that show spectral responses upon binding Ca2+ have enabled researchers to investigate changes in intracellular free Ca2+ concentrations by using fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence spectroscopy and fluorescence microplate readers. Spectral Data: lambdaex 330nm; lambdaem 450nm (with Calcium), lambdaex 356nm; lambdaem 478nm in methanol.
MDL:
MFCD00036955
Molecular Formula:
C47H51N3O22
Molecular Weight:
1009.93
Package Type:
Vial
Product Description:
INDO 1-AM is a popular non-invasive UV-excitable calcium indicator. It is the cell-permeable ester derivative of INDO 1. After crossing the cell membrane, INDO 1-AM is rapidly hydrolyzed by cytoplasmic esterases to produce the ratiometric fluorescent calcium indicator INDO 1, which remains trapped within the cell. INDO 1/AM has been used to selectively monitor Ca2+ levels in mitochondria and in the cytosol. INDO 1 is ideal for analyses using flow cytometry, as it uses a single excitation source (usually the 351-364nm spectral lines of the argon-ion laser). In contrast to FURA 1, INDO 1 has a dual emission peak. The emission of INDO 1 shifts to 400nm (when bound to Ca2+) from 480nm in Ca2+-free environments. INDO 1 is prone to photobleaching, which limits its usefulness in methods involving microscopy. Calcium measurement is critical for numerous biological investigations. Fluorescent probes that show spectral responses upon binding Ca2+ have enabled researchers to investigate changes in intracellular free Ca2+ concentrations by using fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence spectroscopy and fluorescence microplate readers. Spectral Data: lambdaex 330nm; lambdaem 450nm (with Calcium), lambdaex 356nm; lambdaem 478nm in methanol.
Purity:
>90% (HPLC)
SMILES:
CC1=CC(OCCOC2=CC(C3=CC(C=CC(C(OCOC(C)=O)=O)=C4)=C4N3)=CC=C2N(CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)=C(N(CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)CC(OCOC(C)=O)=O)C=C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO or methanol.
Source / Host:
Synthetic.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Fluorescent Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
41105331
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
(1) G. Grynkiewicz, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 260, 3440 (1985) | (2) M. Lopez, et al.; Cytometry 10, 165 (1989) | (3) J.P. Grierson, et al.; J. Neurophysiol. 67, 704 (1992) | (4) E.J. Griffiths, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. 273, C37 (1997) | (5) R.M. Paredes, et al.; Meth. A Comp. Meth. Enzymol. 46, 143 (2008) | (6) Z. Zhou, et al.; J. Physiol. 507, 379 (1998) | (7) S. Bailey & P.J. Macardle; J. Immunol. Meth. 311, 220 (2006) | (8) A. Nelemans; Methods Mol. Biol. 312, 47 (2006) | (9) R.W. Sabnis; Handbook of biological dyes and stains (2010)