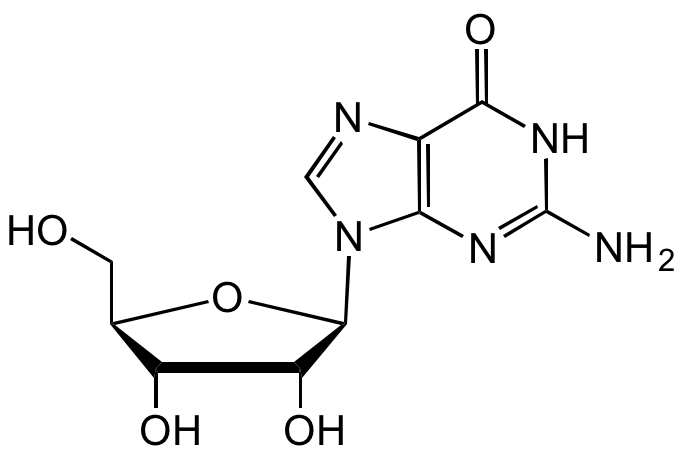
Guanosine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-G0035-G005 | 5 g | £53.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-G0035-G050 | 50 g | £89.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-G0035-G100 | 100 g | £145.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
Short Term: +4°C. Long Term: +4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
9-beta-D-Ribofuranosyl-guanine; Guanine-9-beta-D-ribofuranoside; 2-Amino-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-9H-purine-6-(1H)-one
Appearance:
White to light yellow powder.
CAS:
118-00-3
Class:
6.1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS06
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H301
InChi:
InChI=1S/C10H13N5O5/c11-10-13-7-4(8(19)14-10)12-2-15(7)9-6(18)5(17)3(1-16)20-9/h2-3,5-6,9,16-18H,1H2,(H3,11,13,14,19)/t3-,5-,6-,9-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UUOKFMHZSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 118-00-3. Formula: C10H13N5O5. MW: 283.24. Synthetic. Purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a beta-N9-glycosidic bond. Can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). Guanosine has important functions in cell metabolism and a protective role in response to degenerative diseases or injury with neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects. Required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA message by cutting at both ends, re-ligating, and leaving just the exons on either side to be translated into protein.
MDL:
MFCD00010182
Molecular Formula:
C10H13N5O5
Molecular Weight:
283.24
Package Type:
Vial
PG:
III
Precautions:
P301, P310
Product Description:
Purine nucleoside comprising guanine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) ring via a beta-N9-glycosidic bond. Can be phosphorylated to become guanosine monophosphate (GMP), cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and guanosine triphosphate (GTP). These forms play important roles in various biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). Guanosine has important functions in cell metabolism and a protective role in response to degenerative diseases or injury with neurotrophic and neuroprotective effects. Required for an RNA splicing reaction in mRNA, when a "self-splicing" intron removes itself from the mRNA message by cutting at both ends, re-ligating, and leaving just the exons on either side to be translated into protein.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Danger
SMILES:
O[C@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@H](N2C(N=C(N)NC3=O)=C3N=C2)O[C@@H]1CO
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in formic acid:water (1:1) (~50mg/ml).
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
UN 2811
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
(1) M. Rathbone, et al.; Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 27, 666 (2008) | (2) D. Lanznaster, et al.; Aging Dis. 7, 657 (2016)