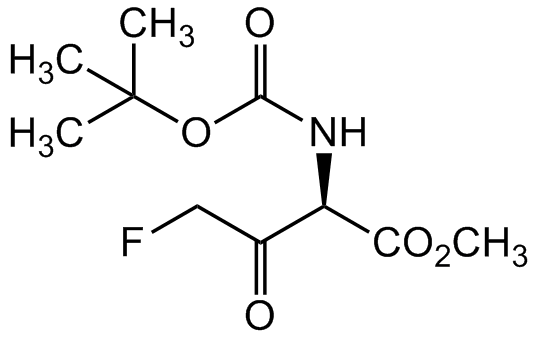
Boc-Asp(OMe)-FMK
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CP3-0030-M001 | 1 mg | £80.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CP3-0030-M005 | 5 mg | £290.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
Boc-D(OMe)-FMK; Boc-D-FMK; BAF
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
187389-53-3
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
InChi:
InChI=1S/C10H16FNO5/c1-10(2,3)17-9(15)12-7(6(13)5-11)8(14)16-4/h7H,5H2,1-4H3,(H,12,15)
InChiKey:
IPYYWMLWOBWDDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 187389-53-3. Formula: C11H18FNO5. MW: 263.3. Synthetic. Cell permeable, irreversible, broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor. Inhibits non-caspase cysteine proteases, as well as cathepsins H and L. Can be used for in vitro and in vivo studies. Contains a methyl ester group, which facilitates uptake by cells and subsequently is removed by cytoplasmic esterases, leaving the functional inhibitor. Inhibits the pro-apoptotic effect of TNF-alpha (IC50=39µM). Shown to reduce the activation of NF-kB, suppresses the phosphorylation of IkBalpha and inhibits TNF-induced expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. Blocks hepatocyte apoptosis in vivo. Neuroprotective.
MDL:
MFCD03453073
Molecular Formula:
C11H18FNO5
Molecular Weight:
263.3
Other data:
Prepare a 20mM stock solution of the caspase inhibitor in DMSO. Add 1µl of above stock solutions to 1ml of culture medium containing cells to give 20µM final concentration. We recommend to ensure the residual amount of DMSO is insignificant (<0.1%), since it may have physiological effects at low concentrations and thus masking the effect of the ICE-protease inhibitor Boc-D(OMe)-FMK. For in vivo experiments extending for 12 to 48 hours, fresh inhibitor may have to be added (injected) due to inactivation by reaction with cysteine protease.
Package Type:
Plastic Vial
Product Description:
Cell permeable, irreversible, broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor. Inhibits non-caspase cysteine proteases, as well as cathepsins H and L. Can be used for in vitro and in vivo studies. Contains a methyl ester group, which facilitates uptake by cells and subsequently is removed by cytoplasmic esterases, leaving the functional inhibitor. Inhibits the pro-apoptotic effect of TNF-alpha (IC50=39µM). Shown to reduce the activation of NF-kB, suppresses the phosphorylation of IkBalpha and inhibits TNF-induced expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. Blocks hepatocyte apoptosis in vivo. Neuroprotective.
Purity:
>98%
Sequence:
Boc-Asp(OMe)-fluoromethylketone
SMILES:
FCC([C@@H](NC(OC(C)(C)C)=O)C(OC)=O)=O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in ethanol (5mg/ml), DMSO or DMF (both 30mg/ml).
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 3 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Different interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme (ICE) family protease requirements for the apoptotic death of T lymphocytes triggered by diverse stimuli: A. Sarin, et al.; J. Exp. Med. 184, 2445 (1996) | A DEVD-inhibited caspase other than CPP32 is involved in the commitment of cerebellar granule neurons to apoptosis induced by K+ deprivation: S.R. D'Mello, et al.; J. Neurochem. 70, 1809 (1998) | Caspase inhibitor BD-fmk distinguishes transforming growth factor beta-induced apoptosis from growth inhibition: T.L. Brown, et al.; Cell Growth Differ. 9, 869 (1998) | Function of caspases in regulating apoptosis caused by erythropoietin deprivation in erythroid progenitors: P.A. Gregoli & M.C. Bondurant; J.Cell Physiol. 178, 133 (1999) | Caspase inhibitors promote the survival of avulsed spinal motoneurons in neonatal rats: Y.M. Chan, et al.; Neurorep. 12, 541 (2001) | z-VAD-fmk augmentation of TNFalpha-stimulated neutrophil apoptosis is compound specific and does not involve the generation of reactive oxygen species: A.S. Cowburn, et al.; Blood 105, 2970 (2005) | Broad-spectrum caspase inhibitors: From myth to reality? D. Chauvier, et al.; Cell Death Diff. 14, 387 (2007) | boc-Aspartyl(OMe)-fluoromethylketone attenuates mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and delays brain tissue loss after traumatic brain injury in rats: R.S. Clark, et al.; J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 27, 316 (2007) | Effect of Boc-D-Fmk on hepatocyte apoptosis after bile duct ligation in rat and survival rate after endotoxin challenge: S.M. Sheen-Chen, et al.; J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 23, 1276 (2008) | TNF induces caspase-dependent inflammation in renal endothelial cells through a Rho- and myosin light chain kinase-dependent mechanism: X. Wu, et al.; Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 297, F316 (2009) | Pharmacological caspase inhibitors: research towards therapeutic perspectives: J. Kudelova, et al.; J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 66, 473 (2015) (Review)