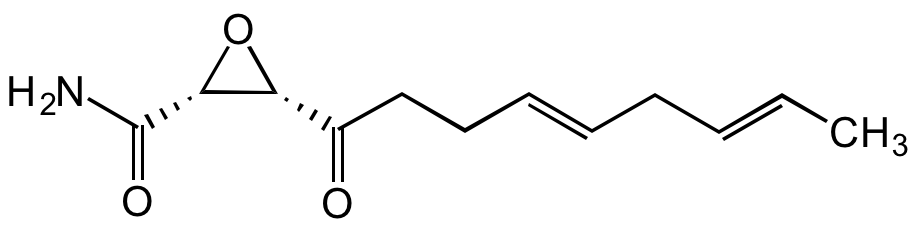
Cerulenin
Product Code: AG-CN2-0513
Product Group: Antibiotics and Other Antimicrobials
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0513-M005 | 5 mg | £140.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
Ambient
Storage:
-200
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
2R,3S-Epoxy-4-oxo-7,10-dodecadienamide; Helicocerin
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
17397-89-6
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from light.Protect from moisture and oxygen.
Hazards:
H302
InChi:
InChI=1S/C12H17NO3/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9(14)10-11(16-10)12(13)15/h2-3,5-6,10-11H,4,7-8H2,1H3,(H2,13,15)/b3-2+,6-5+/t10-,11-/m1/s1
InChiKey:
GVEZIHKRYBHEFX-NQQPLRFYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 17397-89-6. Formula: C12H17NO3. MW: 223.3. Isolated from Cephalosporium caerulens. Antibiotic and antifungal compound. Inhibitor of bacterial fatty acid synthesis (inhibits FabH, FabB and FabF condensation enzymes). Irreversible fatty acid synthase (FAS) inhibitor. Inhibits sterol and fatty acid biosynthesis. In fatty acid synthesis, reported to bind in equimolar ratio to beta-keto-acyl-ACP synthase, thus inhibiting protein acylation. In sterol synthesis, inhibits HMG-CoA synthetase activity. Palmitoylation (a post-translational lipidation) inhibitor. Anticancer agent. Apoptosis inducer in tumor cell lines, with upregulated expression and activity of fatty acid synthase (FAS). Shown to induce apoptosis via disruption of the interaction between AIF and Hexokinase II (HKII). Necroptosis inhibitor by blocking very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) synthesis and accumulation, which is important in the process of necroptosis (RIP1-dependent cell death). Also leads to profound weight loss and feeding inhibition in both high-fat diet wild type obese and leptin-deficient ob/ob mice.
MDL:
MFCD00083595
Molecular Formula:
C12H17NO3
Molecular Weight:
223.3
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P264, P270, P301, P312, P330, P501
Product Description:
Antibiotic and antifungal compound. Inhibitor of bacterial fatty acid synthesis (inhibits FabH, FabB and FabF condensation enzymes). Irreversible fatty acid synthase (FASN) inhibitor. Inhibits sterol and fatty acid biosynthesis. In fatty acid synthesis, reported to bind in equimolar ratio to beta-keto-acyl-ACP synthase, thus inhibiting protein acylation. In sterol synthesis, inhibits HMG-CoA synthetase activity. Palmitoylation (a post-translational lipidation) inhibitor. Anticancer agent. Apoptosis inducer in tumor cell lines, with upregulated expression and activity of fatty acid synthase (FAS). Shown to induce apoptosis via disruption of the interaction between AIF and Hexokinase II (HKII). Necroptosis inhibitor by blocking very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) synthesis and accumulation, which is important in the process of necroptosis (RIP1-dependent cell death). Also leads to profound weight loss and feeding inhibition in both high-fat diet wild type obese and leptin-deficient ob/ob mice.
Purity:
>98%
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
O=C(CC/C=C/C/C=C/C)[C@@H]1[C@H](C(N)=O)O1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (25mg/ml), ethanol (20mg/ml) or DMF (25mg/ml).
Source / Host:
Isolated from Cephalosporium caerulens.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Studies on cerulenin, 3. Isolation and physico-chemical properties of cerulenin: Y. Sato, et al.; J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 200, 344 (1967) | Inhibition of fatty acid synthetases by the antibiotic cerulenin: D. Vance, et al.; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 48, 649 (1972) | The antibiotic cerulenin, a novel tool for biochemistry as an inhibitor of fatty acid synthesis: S. Omura; Bacteriol. Rev. 40, 681 (1976) (Review) | Cerulenin is a potent inhibitor of antigen processing by antigen-presenting cells: L.D. Falo, et al.; J. Immunol. 139, 3918 (1987) | Modulation of insulin secretion from normal rat islets by inhibitors of the post-translational modifications of GTP-binding proteins: S.A. Metz, et al.; Biochem. J. 295, 31 (1993) | Inhibitory effects of cerulenin on protein palmitoylation and insulin internalization in rat adipocytes: A.L. Jochen, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1259, 65 (1995) | Reduced food intake and body weight in mice treated with fatty acid synthase inhibitors: T.M. Loftus, et al.; Science 288, 2379 (2000) | Cerulenin, an inhibitor of protein acylation, selectively attenuates nutrient stimulation of insulin release: a study in rat pancreatic islets: H. Yajima, et al.; Diabetes 49, 712 (2000) | Cerulenin mimics effects of leptin on metabolic rate, food intake, and body weight independent of the melanocortin system, but unlike leptin, cerulenin fails to block neuroendocrine effects of fasting: H. Makimura, et al.; Diabetes 50, 733 (2001) | Key role of mitochondria in cerulenin-mediated apoptosis: S.J. Heiligtag, et al.; Cell Death Differ. 9, 1017 (2002) | Fatty acid synthase inhibitors cerulenin and C75 retard growth and induce caspase-dependent apoptosis in human melanoma A-375 cells: T.S. Ho, et al.; Biomed. Pharmacother. 61, 578 (2007) | Fatty acid synthase inhibitor cerulenin suppresses liver metastasis of colon cancer in mice: S. Murata, et al.; Cancer Sci. 101, 1861 (2010) | Cerulenin-induced apoptosis is mediated by disrupting the interaction between AIF and hexokinase II: N.Y. Jeong & Y.H. Yoo; Int. J. Oncol. 40, 1949 (2012) | Very long chain fatty acids are functionally involved in necroptosis: L.R. Parisi, et al.; Cell Chem. Biol. 24, 1445 (2017)