BPTES
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CR1-3690-M001 | 1 mg | £35.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3690-M005 | 5 mg | £85.00 |
Quantity:
| AG-CR1-3690-M025 | 25 mg | £235.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Target Species: Universal
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
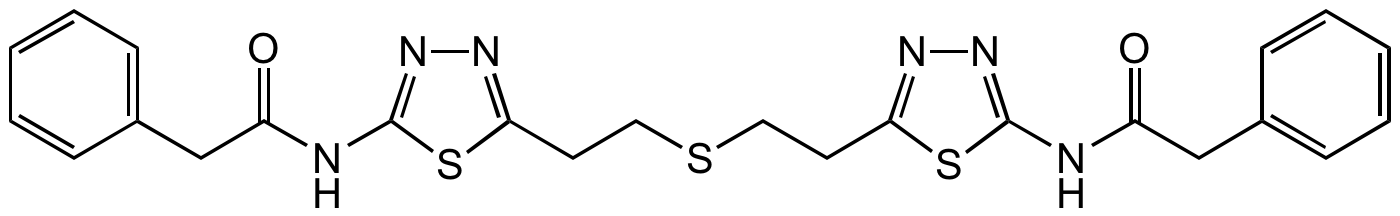
Bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide
Appearance:
White to off-white solid.
CAS:
314045-39-1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.Protect from moisture and oxygen.
Hazards:
H319
InChi:
InChI=1S/C24H24N6O2S3/c31-19(15-17-7-3-1-4-8-17)25-23-29-27-21(34-23)11-13-33-14-12-22-28-30-24(35-22)26-20(32)16-18-9-5-2-6-10-18/h1-10H,11-16H2,(H,25,29,31)(H,26,30,32)
InChiKey:
MDJIPXYRSZHCFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 314045-39-1. Formula: C24H24N6O2S3. MW: 524.7. . Selective, allosteric non-competitive inhibitor of glutaminase 1 (GLS1), selective for GLS1 over GLS2, glutamate dehydrogenase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, consequently inhibiting glutaminolysis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Glutaminase converts glutamine to glutamate, which is an important excitatory neurotransmitter in brain and can be further oxidized to alpha-ketoglutarate to feed the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and to glutathione, which is important for controlling the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), particularly important for cancer cell growth. Anticancer agent. Increases the production of reactive oxygen species and reduces ATP levels in hypoxic cells, induces cell death of P493 human lymphoma B cells in vitro and delays tumor xenograft growth in vivo.
MDL:
MFCD01079848
Molecular Formula:
C24H24N6O2S3
Molecular Weight:
524.7
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P305+P351+P338
Product Description:
Selective, allosteric non-competitive inhibitor of glutaminase 1 (GLS1), selective for GLS1 over GLS2, glutamate dehydrogenase, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, consequently inhibiting glutaminolysis. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Glutaminase converts glutamine to glutamate, which is an important excitatory neurotransmitter in brain and can be further oxidized to alpha-ketoglutarate to feed the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and to glutathione, which is important for controlling the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS), particularly important for cancer cell growth. Anticancer agent. Increases the production of reactive oxygen species and reduces ATP levels in hypoxic cells, induces cell death of P493 human lymphoma B cells in vitro and delays tumor xenograft growth in vivo.
Purity:
>95% (HPLC)
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
O=C(CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC2=NN=C(CCSCCC3=NN=C(NC(CC4=CC=CC=C4)=O)S3)S2
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml) or DMF (10mg/ml). Sparingly soluble in aqueous buffers.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Novel mechanism of inhibition of rat kidney-type glutaminase by bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,2,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide (BPTES): M.M. Robinson, et al.; Biochem. J. 406, 407 (2007) | Inhibition of glutaminase preferentially slows growth of glioma cells with mutant IDH1: M.J. Seltzer, et al.; Cancer Res. 70, 8981 (2010) | Full-length human glutaminase in complex with an allosteric inhibitor: B. DeLaBarre, et al.; Biochemistry 50, 10764 (2011) | BPTES inhibition of hGA(124-551), a truncated form of human kidney-type glutaminase: E.W. Hartwick & N.P. Curthoys; J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 27, 861 (2012) | Glucose-independent glutamine metabolism via TCA cycling for proliferation and survival in B cells: A. Le, et al.; Cell Metab. 15, 110 (2012) | Design, synthesis, and pharmacological evaluation of bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,2,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide 3 (BPTES) analogs as glutaminase inhibitors: K. Shukla, et al.; J. Med. Chem. 55, 10551 (2012) | Availability of the key metabolic substrates dictates the respiratory response of cancer cells to the mitochondrial uncoupling: A.V. Zhdanov, et al.; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1837, 51 (2014) | Small molecule glutaminase inhibitors block glutamate release from stimulated microglia: A.G. Thomas, et al.; BBRC 443, 32 (2014) | Targeted inhibition of tumor-specific glutaminase diminishes cell-autonomous tumorigenesis: Y. Xiang, et al.; J. Clin. Invest. 125, 2293 (2015) | Design and evaluation of novel glutaminase inhibitors: L.A. McDermott, et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 24, 1819 (2016) | Glutaminase 1 inhibition reduces thymidine synthesis in NSCLC: J.S. Lee, et al.; BBRC 477, 374 (2016) | Inhibition of Glutaminolysis Inhibits Cell Growth via Down-regulating Mtorc1 Signaling in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma: X. Ye, et al.; Anticancer Res. 36, 6021 (2016) | A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists: L.A. O'Neill, et al.; Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 553 (2016) (Review) | Characterization of the interactions of potent allosteric inhibitors with glutaminase C, a key enzyme in cancer cell glutamine metabolism: Q. Huang, et al.; J. Biol. Chem. 293, 3535 (2018)
Related Products
| Product Name | Product Code | Supplier | Radicicol | AG-CN2-0021 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shikonin | AG-CN2-0487 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2-Deoxy-D-glucose | AG-CR1-3681 | AdipoGen Life Sciences | Summary Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||