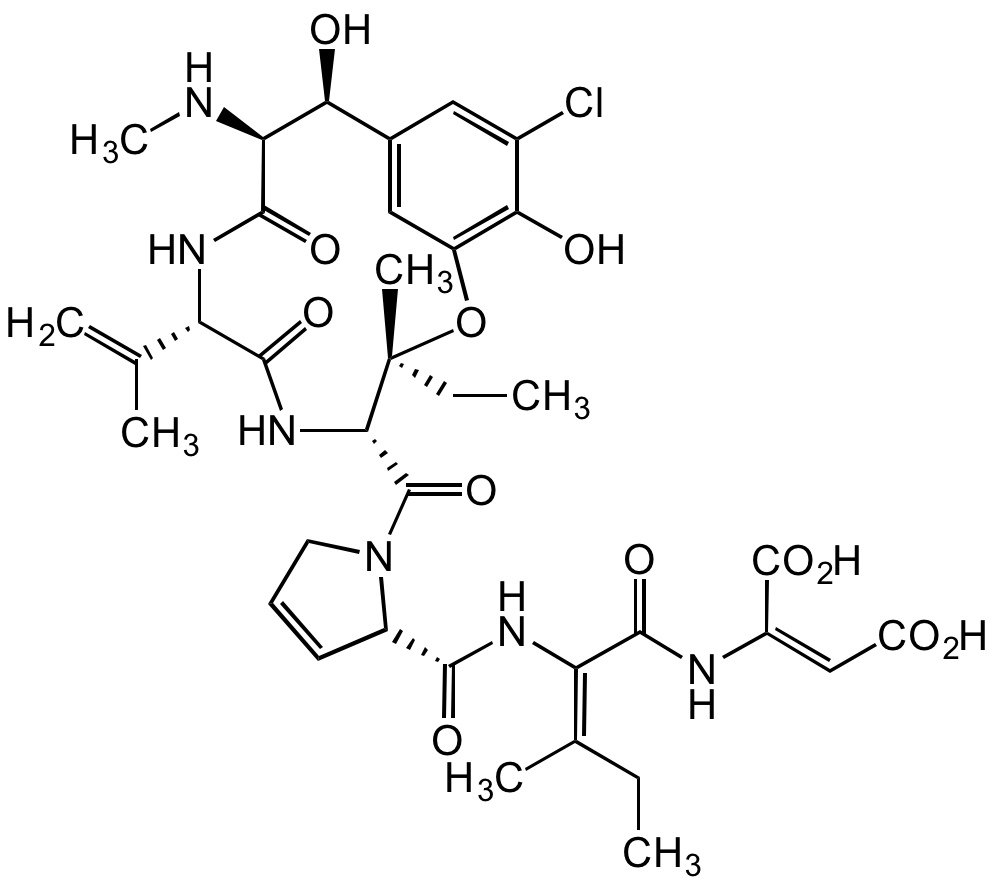
Phomopsin A
Product Code: AG-CN2-0515
Product Group: Natural Products and Extracts
Supplier: AdipoGen Life Sciences
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| AG-CN2-0515-M001 | 1 mg | £370.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
-20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
PHO-A; NSC 381839
Appearance:
White solid.
CAS:
64925-80-0
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
solid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07,GHS08
Handling Advice:
Keep cool and dry.
Hazards:
H302, H312, H332, H351
InChi:
InChI=1S/C36H45ClN6O12/c1-8-17(5)25(32(50)39-20(35(53)54)15-23(44)45)41-30(48)21-11-10-12-43(21)34(52)29-36(6,9-2)55-22-14-18(13-19(37)28(22)47)27(46)26(38-7)33(51)40-24(16(3)4)31(49)42-29/h10-11,13-15,21,24,26-27,29,38,46-47H,3,8-9,12H2,1-2,4-7H3,(H,39,50)(H,40,51)(H,41,48)(H,42,49)(H,44,45)(H,53,54)/b20-15+,25-17+/t21-,24-,26-,27-,29-,36-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
FAFRRYBYQKPKSY-KBIMZEDXSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 64925-80-0. Formula: C36H45ClN6O12. MW: 789.2. Isolated from Phomopsis leptostromiformis. Macrocyclic heptapeptide mycotoxin. Potent anti-mitotic compound that can cause cell death. Microtubule assembly inhibitor. Binds selectively to dimeric tubulin, inhibiting the formation of the microtubule spindle to block cell division. Binds at a site different from the colchicine binding site and overlapping the vinblastine binding site. Inhibits tubulin-dependent GTP hydrolysis. Binds beta-tubulin from higher organisms but not alpha-tubulin or fungal mycelial tubulin. Causes lupinosis (a degenerative disorder) in livestock fed infected lupins.
MDL:
MFCD00467142
Molecular Formula:
C36H45ClN6O12
Molecular Weight:
789.2
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P261, P301, P312, P302, P352, P304, P340
Product Description:
Macrocyclic heptapeptide mycotoxin. Potent anti-mitotic compound that can cause cell death. Microtubule assembly inhibitor. Binds selectively to dimeric tubulin, inhibiting the formation of the microtubule spindle to block cell division. Binds at a site different from the colchicine binding site and overlapping the vinblastine binding site. Inhibits tubulin-dependent GTP hydrolysis. Binds beta-tubulin from higher organisms but not alpha-tubulin or fungal mycelial tubulin. Causes lupinosis (a degenerative disorder) in livestock fed infected lupins.
Purity:
>98% (HPLC, TLC)
Signal Word:
Warning
SMILES:
ClC1=CC([C@H](O)[C@@H]2NC)=CC(O[C@@](C)(CC)[C@H](C(N3CC=C[C@H]3C(N/C(C(N/C(C(O)=O)=C/C(O)=O)=O)=C(C)/CC)=O)=O)NC([C@H](C(C)=C)NC2=O)=O)=C1O
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in DMSO (10mg/ml), ethanol, methanol (5mg/ml) or DMF.
Source / Host:
Isolated from Phomopsis leptostromiformis.
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Natural Products/Extracts
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at -20°C.
References
Interaction of phomopsin A and related compounds with purified sheep brain tubulin: E. Lacey, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 36, 2133 (1987) | Effect of phomopsin A on the alkylation of tubulin: R.F. Luduena, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1603 (1990) | Dolastatin 10, a powerful cytostatic peptide derived from a marine animal. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization mediated through the vinca alkaloid binding domain: R. Bai, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 39, 1941 (1990) | Binding selectivity of rhizoxin, phomopsin A, vinblastine, and ansamitocin P-3 to fungal tubulins: differential interactions of these antimitotic agents with brain and fungal tubulins: Y. Li, et al.; BBRC 187, 722 (1992) | Interaction of phomopsin A with porcine brain tubulin. Inhibition of tubulin polymerization and binding at a rhizoxin binding site: Y. Li, et al.; Biochem. Pharmacol. 43, 219 (1992) | Natural products which interact with tubulin in the vinca domain: maytansine, rhizoxin, phomopsin A, dolastatins 10 and 15 and halichondrin B: E. Hamel; Pharmacol. Ther. 55, 31 (1992) | Interaction of phomopsin A with normal and subtilisin-treated bovine brain tubulin: A.R. Chaudhuri & R.F. Luduena; J. Protein Chem. 16, 99 (1997) | Localization of the antimitotic peptide and depsipeptide binding site on beta-tubulin: A. Mitra & D. Sept; Biochemistry 43, 13955 (2004) | Structural insight into the inhibition of tubulin by vinca domain peptide ligands: A. Cormier, et al.; EMBO Rep. 9, 1101 (2008)