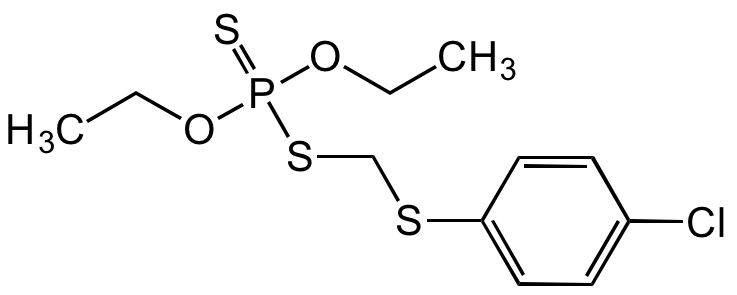
Carbophenothion
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-C0683-M500 | 500 mg | £72.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
+4°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
S-(4-Chlorophenylthiomethyl) O,O-diethyl phosphorodithioate; Stauffer R1303; Trithion; NSC 231691; ENT 23,708; Ethyl Carbophenothion
Appearance:
Colorless to yellowish liquid.
CAS:
786-19-6
Class:
6.1
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS06,GHS09
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H300, H311, H410
InChi:
InChI=1S/C11H16ClO2PS3/c1-3-13-15(16,14-4-2)18-9-17-11-7-5-10(12)6-8-11/h5-8H,3-4,9H2,1-2H3
InChiKey:
VEDTXTNSFWUXGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 786-19-6. Formula: C11H16ClO2PS3. MW: 342.87. . An organophosphate pesticide. Insecticide and acaricide used in the agriculture industry. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor in the nervous system with subsequent accumulation of toxic levels of acetylcholine (ACh). Used for citrus fruits against insects. Compound can be used as analytical reference material.
MDL:
MFCD00128009
Molecular Formula:
C11H16ClO2PS3
Molecular Weight:
342.87
Package Type:
Vial
PG:
II
Precautions:
P264-P273-P280-P301 + P310-P312-P501
Product Description:
An organophosphate pesticide. Insecticide and acaricide used in the agriculture industry. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor in the nervous system with subsequent accumulation of toxic levels of acetylcholine (ACh). Used for citrus fruits against insects. Compound can be used as analytical reference material.
Purity:
>98% (GC)
Signal Word:
Danger
SMILES:
ClC1=CC=C(SCSP(OCC)(OCC)=S)C=C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Miscible soluble in most organic solvents including alcohols and ethers. Insoluble in water.
Transportation:
Excepted Quantity
UN Nummer:
2810
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +4°C.
References
(1) C.E. Hearn, et al.; Br. J. Ind. Med. 18, 231 (1961) | (2) J.J. Older & R.L. Hatcher; JAMA 209, 1328 (1969) | (3) J.R. DeBaun & J.J. Menn; Science 191, 187 (1976) | (4) G.E. Westlake, et al.; Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2, 151 (1978) | (5) M. Mezcua, et al.; Food Chem. 112, 221 (2009)