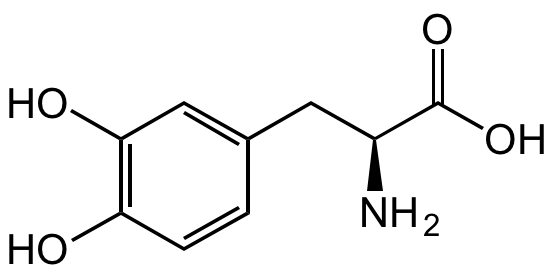
3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine
| Code | Size | Price |
|---|
| CDX-D0465-G025 | 25 g | £84.00 |
Quantity:
| CDX-D0465-G100 | 100 g | £230.00 |
Quantity:
Prices exclude any Taxes / VAT
Overview
Regulatory Status: RUO
Shipping:
AMBIENT
Storage:
+20°C
Images
Documents
Further Information
Alternate Names/Synonyms:
3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine; L-DOPA; 3-Hydroxy-L-tyrosine; Levodopa
Appearance:
White to off-white powder.
CAS:
59-92-7
EClass:
32160000
Form (Short):
liquid
GHS Symbol:
GHS07
Handling Advice:
Protect from light and moisture.
Hazards:
H302, H315, H319, H335
InChi:
InChI=1S/C9H11NO4/c10-6(9(13)14)3-5-1-2-7(11)8(12)4-5/h1-2,4,6,11-12H,3,10H2,(H,13,14)/t6-/m0/s1
InChiKey:
WTDRDQBEARUVNC-LURJTMIESA-N
Long Description:
Chemical. CAS: 59-92-7. Formula: C9H11NO4. MW: 197.19. Synthetic. Metabolic precursor of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. This amino acid is produced from L-tyrosine by tyrosine hydroxylase and metabolized by catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). L-DOPA is capable of crossing the blood brain barrier where it is converted to dopamine. Formulations containing L-DOPA have been used to increase dopamine concentrations in the brain as a treatment for Parkinson?s disease and stroke recovery. Mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. Used for the treatment of Parkinson?s disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia. In addition it is used, as a cell adhesion molecule in serum-free cultures of anchorage-dependent mammalian cells, to prevent surfaces from fouling by bonding antifouling polymers to a susceptible substrate or to stain melanocytes.
MDL:
MFCD00002598
Molecular Formula:
C9H11NO4
Molecular Weight:
197.19
Package Type:
Vial
Precautions:
P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338
Product Description:
Metabolic precursor of the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. This amino acid is produced from L-tyrosine by tyrosine hydroxylase and metabolized by catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). L-DOPA is capable of crossing the blood brain barrier where it is converted to dopamine. Formulations containing L-DOPA have been used to increase dopamine concentrations in the brain as a treatment for Parkinson?s disease and stroke recovery. Mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. Used for the treatment of Parkinson?s disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia. In addition it is used, as a cell adhesion molecule in serum-free cultures of anchorage-dependent mammalian cells, to prevent surfaces from fouling by bonding antifouling polymers to a susceptible substrate or to stain melanocytes.
Purity:
>98%
Signal word:
Warning
SMILES:
OC1=C(O)C=CC(C[C@H](N)C(O)=O)=C1
Solubility Chemicals:
Soluble in water (5-10mM), acidic and basic solutions.
Source / Host:
Synthetic
Transportation:
Non-hazardous
UNSPSC Category:
Biochemical Reagents
UNSPSC Number:
12352200
Use & Stability:
Stable for at least 2 years after receipt when stored at +20°C.
References
(1) O. Hornykiewicz; Life Sci. 15, 1249 (1974) (Review) | (2) Y. Misu, et al.; Adv. Pharmacol. 32, 427 (1995) (Review) | (3) J.G. Nutt; Adv. Neurol. 69,493 (1996) (Review) | (4) R.M. Kostrzewa, et al.; Amino Acids 23, 57 (2002) (Review) | (5) N.B. Mercuri & G. Bernardi; Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 26, 341 (2005) (Review) | (6) M.A. Mena, et al.; Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 9, 880 (2009) (Review) | (7) H.I. Berends, et al.; Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 45, 621 (2009) (Review) | (8) H. Iderberg, et al.; Neuroscience 211, 13 (2012) (Review) | (9) Y. Huang, et al.; Electrochim. Acta 113, 564 (2013) | (10) P. Huot, et al.; Pharmacol. Rev. 65, 171 (2013) (Review) | (11) J. Tang, et al.; Cytotechnology 66, 891 (2014) | (12) G. Fichman, et al.; ACS Nano. 8, 7220 (2014) | (13) M.M. Conti, et al.; Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. (Epub ahead of print) (2018) (Review)